Vector Form Physics
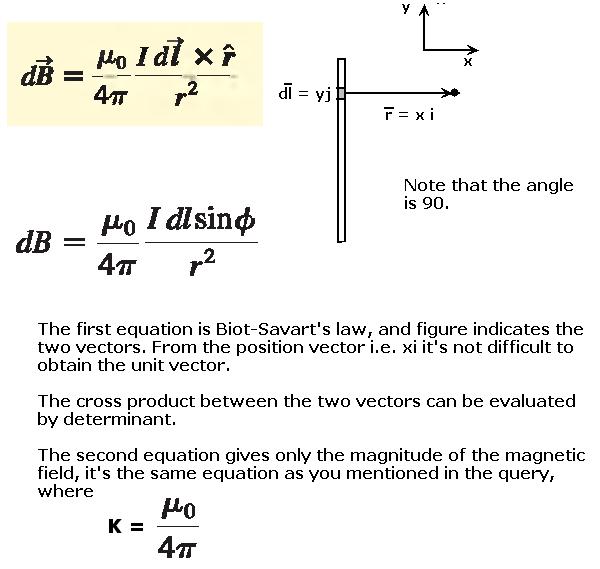
Vector Form Physics - Web the vector form is $$ \vec{f} = m \left( \vec{\omega} \times (\vec{\omega} \times \vec{r}) \right) \tag{1}$$ where $m$ is the mass of the object, $\vec{r}$ is the position of the center of mass relative to the axis of rotation, and $\vec{\omega}$ is rotational (orbital) velocity of the body. Although a vector has magnitude and direction, it does not have position. Vectors can be added to other vectors according to vector algebra. N1sinθ1 =n2sinθ2 n 1 sin θ 1 = n 2 sin θ 2. It's a fairly clear and visual way to show the magnitude and direction of a vector on a graph. Web what do vectors and scalars have in common? Where θ1 θ 1 is the angle of incidence and θ2 θ 2 the angle of refraction. Web snell's law of refraction at the interface between 2 isotropic media is given by the equation: Quantity with magnitude, no direction. Web in physics, we often use the terms force, speed, velocity and work, and these quantities are classified as a scalar or vector quantities.
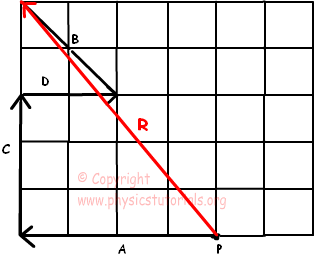
Web 13k 844k views 2 years ago new physics video playlist this physics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into vectors. Web in physics, vectors that represent force and velocity are two common examples of vectors. But some vectors are directed northeast (at a 45 degree angle); Web identify the magnitude and direction of a vector. What relative direction between them produces the resultant with the greatest magnitude? Where θ1 θ 1 is the angle of incidence and θ2 θ 2 the angle of refraction. Adding vectors in magnitude & direction form. These are known as radial and angular components of a vector, and the polar form of the vector as shown in the diagram above is ⃑ 𝑣 = ( 𝑟, 𝜃). Web resolving vectors into their scalar components (i.e., finding their scalar components) and expressing them analytically in vector component form (given by equation 2.19) allows us to use vector algebra to find sums or differences of many vectors analytically (i.e., without using graphical methods). N1sinθ1 =n2sinθ2 n 1 sin θ 1 = n 2 sin θ 2.
It explains the differences between scalar and vector quantities. These are known as radial and angular components of a vector, and the polar form of the vector as shown in the diagram above is ⃑ 𝑣 = ( 𝑟, 𝜃). Explain the geometric construction for the. Web 13k 844k views 2 years ago new physics video playlist this physics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into vectors. Suppose you are told to measure your happiness. It's a fairly clear and visual way to show the magnitude and direction of a vector on a graph. What relative direction between them produces the resultant with the smallest magnitude? Web identify the magnitude and direction of a vector. It can be represented by a vector. Web the physical quantities are of two types namely scalars (with the only magnitude) and vectors (those quantities with magnitude and direction).
Vector form of Electric Field Physics(12th) Electrostatics L6
Magnitude & direction form of vectors. In this case, you can never measure your happiness. Web 13k 844k views 2 years ago new physics video playlist this physics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into vectors. Web vectors can be directed due east, due west, due south, and due north. Vectors are a combination of magnitude and direction, and are.
Spice of Lyfe Physics Vector Equations
Force is a vector quantity as it has both magnitude and direction. Vector form is useful to simultaneously represent the magnitude and direction of any physical quantity. Suppose you add two vectors →a and →b. Web vector, in physics, a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. Such as mass, force, velocity, displacement, temperature, etc.
Physics Vector SVG Icon SVG Repo
Web a vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. What is the maximum magnitude? What relative direction between them produces the resultant with the greatest magnitude? N1sinθ1 =n2sinθ2 n 1 sin θ 1 = n 2 sin θ 2. Web vector, in physics, a quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
Vectors
Although a vector has magnitude and direction, it does not have position. It is represented by an arrow of length equal to its magnitude and pointing in the direction of the vector. Explain the geometric construction for the. Web vector, in physics, a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. The magnitude of the vector would mean the force's intensity.
Vectors Part 1 Physics YouTube
N1 n 1 is the refractive index of the optical medium in front of the interface and n2 n 2 is the refractive index of the. And some vectors are even directed northeast, yet more north than east. These are known as radial and angular components of a vector, and the polar form of the vector as shown in the.
Vectors in Physics YouTube
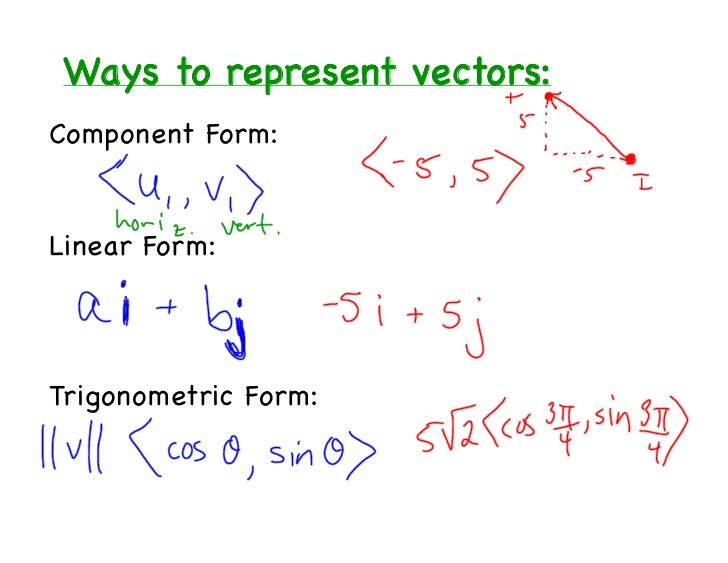
Explain the effect of multiplying a vector quantity by a scalar. Web the physical quantities are of two types namely scalars (with the only magnitude) and vectors (those quantities with magnitude and direction). Web to find the vector in component form given the initial and terminal points, simply subtract the initial point from the terminal point. Express a vector in.
Spice of Lyfe Magnitude Formula Physics Vector
Explain the geometric construction for the. Such as mass, force, velocity, displacement, temperature, etc. N1 n 1 is the refractive index of the optical medium in front of the interface and n2 n 2 is the refractive index of the. Web the vector form is $$ \vec{f} = m \left( \vec{\omega} \times (\vec{\omega} \times \vec{r}) \right) \tag{1}$$ where $m$ is.
Pc 6.3 notes_vectors
Quantity with a magnitude and a direction. Web a vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. Web snell's law of refraction at the interface between 2 isotropic media is given by the equation: Web what are vectors in physics? What is the maximum magnitude?
The Vector Form of Coulomb’s Law of Force [ ]
Magnitude & direction form of vectors. In this case, you can never measure your happiness. Web snell's law of refraction at the interface between 2 isotropic media is given by the equation: The magnitude of the vector would mean the force's intensity or the velocity's related speed. Quantity with magnitude, no direction.
Vectors
Vector form is useful to simultaneously represent the magnitude and direction of any physical quantity. In the first couple of units, all vectors that we discussed were simply directed up, down, left or right. And some vectors are even directed northeast, yet more north than east. What is the maximum magnitude? Although a vector has magnitude and direction, it does.
Magnitude & Direction Form Of Vectors.
Explain the geometric construction for the. It is typically represented by an arrow whose direction is the same as that of the quantity and whose length is proportional to the quantity’s magnitude. Express a vector in component form Web most commonly in physics, vectors are used to represent displacement, velocity, and acceleration.
Web Snell's Law Of Refraction At The Interface Between 2 Isotropic Media Is Given By The Equation:
Same displacement displacement does not describe the object’s path. It's a fairly clear and visual way to show the magnitude and direction of a vector on a graph. It explains the differences between scalar and vector quantities. By jidan / november 1, 2021 a physical quantity is a quantity whose physical properties you can measure.
Web The Vector Form Is $$ \Vec{F} = M \Left( \Vec{\Omega} \Times (\Vec{\Omega} \Times \Vec{R}) \Right) \Tag{1}$$ Where $M$ Is The Mass Of The Object, $\Vec{R}$ Is The Position Of The Center Of Mass Relative To The Axis Of Rotation, And $\Vec{\Omega}$ Is Rotational (Orbital) Velocity Of The Body.
A scalar quantity is a physical quantity with only magnitudes, such as mass and electric charge. Web the vector form is useful to perform numerous arithmetic operations involving vectors. Suppose you are told to measure your happiness. Web identify the magnitude and direction of a vector.
Web 13K 844K Views 2 Years Ago New Physics Video Playlist This Physics Video Tutorial Provides A Basic Introduction Into Vectors.
In this case, you can never measure your happiness. And some vectors are even directed northeast, yet more north than east. What relative direction between them produces the resultant with the greatest magnitude? Power and velocity are both acting in the same way.





![The Vector Form of Coulomb’s Law of Force [ ]](https://s2.studylib.net/store/data/010286221_1-1ed68ddbead41515f19ce45cc0c2c134.png)