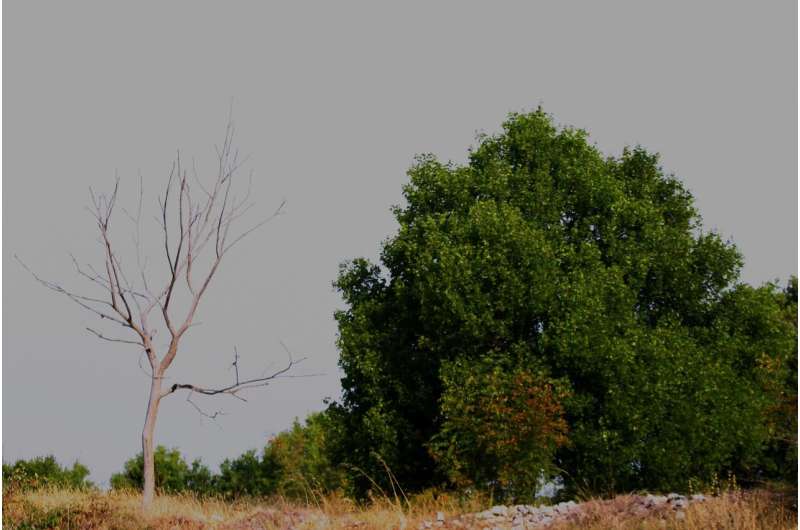
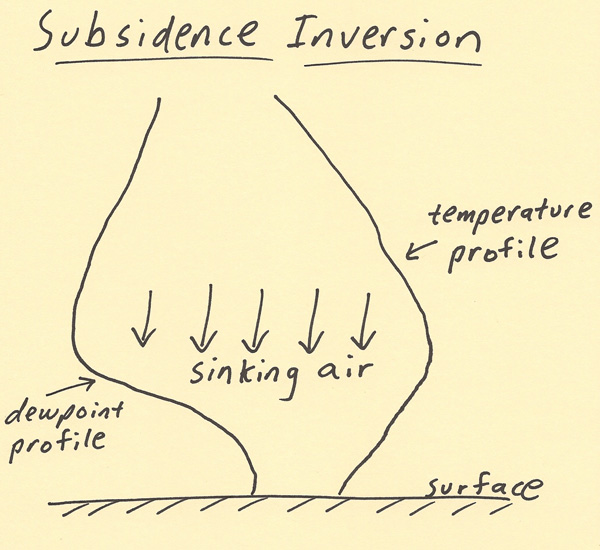
Sinking Or Subsiding Air Cannot Form Clouds Due To The
Sinking Or Subsiding Air Cannot Form Clouds Due To The - C) formation of unstable layers. B) release of latent heat. Web sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to which of the following: Formation of unstable layers b. The heat released when water vapor condenses to form a cloud or when liquid droplets freeze in a cloud: That warmed air starts to rise because, when. Removal of water vapor d. If the air temperature remains constant, evaporation water into the air will ______ the dew point. Formation of unstable layers b. Web 65 sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to the a.
Heated by sunshine, the ground heats the air just above it. Web the three primary ways that clouds dissipate is by (1) the temperature increasing, (2) the cloud mixing with drier air, or (3) the air sinking within the cloud. 65) sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to the:a) release of latent heat.b) loss of particulates. Web up to 20% cash back [solved] sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to the: That warmed air starts to rise because, when. Web 65 sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to the a. Web as warm, moist air rises outdoors, it carries water vapor high into the atmosphere where there is less air pressure. Violent vertical motion can be seen in tornados. Removal of water vapor d. Web sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to which of the following:
A) removal of water vapor. The important difference between liquid droplets and ice crystals in a supercooled cloud is. Violent vertical motion can be seen in tornados. Web up to 20% cash back [solved] sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to the: Web as warm, moist air rises outdoors, it carries water vapor high into the atmosphere where there is less air pressure. That warmed air starts to rise because, when. If the air temperature remains constant, evaporation water into the air will ______ the dew point. Web sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to the. Formation of unstable layers b. Web if the warm air is moist and conditionally unstable, altocumulus and cumulonimbus clouds form, and, frequently, thunderstorms will be embedded in the cloud masses that.
Subsiding Blue Storm by HannahDoma on DeviantArt
The air expands, causing it to cool. 43) sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to the a) loss of particulates b) removal of water vapor c) wanning temperatures d) release of. If the air temperature remains constant, evaporation water into the air will ______ the dew point. The important difference between liquid droplets and ice crystals in a.
HABYTIME MINI LECTURE 42 SUBSIDENCE INVERSION
Heated by sunshine, the ground heats the air just above it. Web 65 sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to the a. Web if the warm air is moist and conditionally unstable, altocumulus and cumulonimbus clouds form, and, frequently, thunderstorms will be embedded in the cloud masses that. Removal of water vapor d. A) removal of water vapor.
(DOC) FORMJ (Notice of sinking shafts and boreholes Manoj Kumar
At other times rising air may. If the air temperature remains constant, evaporation water into the air will ______ the dew point. Web sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to the. A) removal of water vapor. This permits cool dry air above the eye to sink down into the central core of the eye (that is why the.
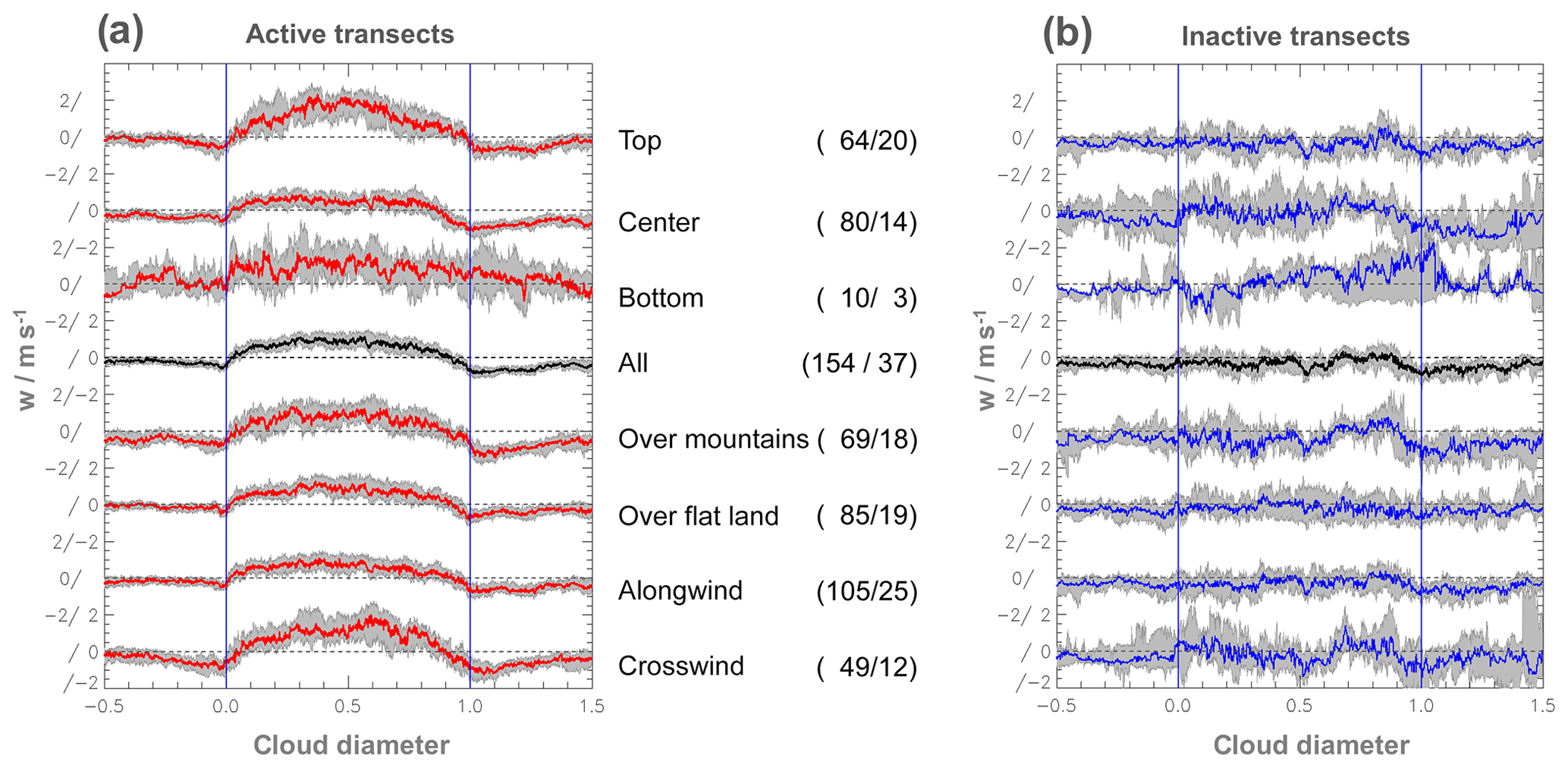
ACP Subsiding shells and the distribution of up and downdraughts in
Web the three primary ways that clouds dissipate is by (1) the temperature increasing, (2) the cloud mixing with drier air, or (3) the air sinking within the cloud. Web sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to the. Web 65 sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to the a. Web sinking or subsiding air cannot form.
Solved 7. Regarding the TAPS project, the first important
Web sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to which of the following: Web if the warm air is moist and conditionally unstable, altocumulus and cumulonimbus clouds form, and, frequently, thunderstorms will be embedded in the cloud masses that. Formation of unstable layers b. If the air temperature remains constant, evaporation water into the air will ______ the dew.
Couldn’t get a photo due to the clouds, but the sound was amazing
Web the three primary ways that clouds dissipate is by (1) the temperature increasing, (2) the cloud mixing with drier air, or (3) the air sinking within the cloud. The heat released when water vapor condenses to form a cloud or when liquid droplets freeze in a cloud: Removal of water vapor d. Web as warm, moist air rises outdoors,.
Subsiding air parcels are among the causes of hot spells
Web sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to the. Removal of water vapor d. Web sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to the warming temperature. 65) sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to the:a) release of latent heat.b) loss of particulates. The important difference between liquid droplets and ice crystals in a supercooled cloud.
ACP Subsiding shells and the distribution of up and downdraughts in
Web some clouds form as air warms up near the earth's surface and rises. Web a)lost heat to the colder air at higher altitudes. The air expands, causing it to cool. Removal of water vapor d. Web up to 20% cash back [solved] sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to the:
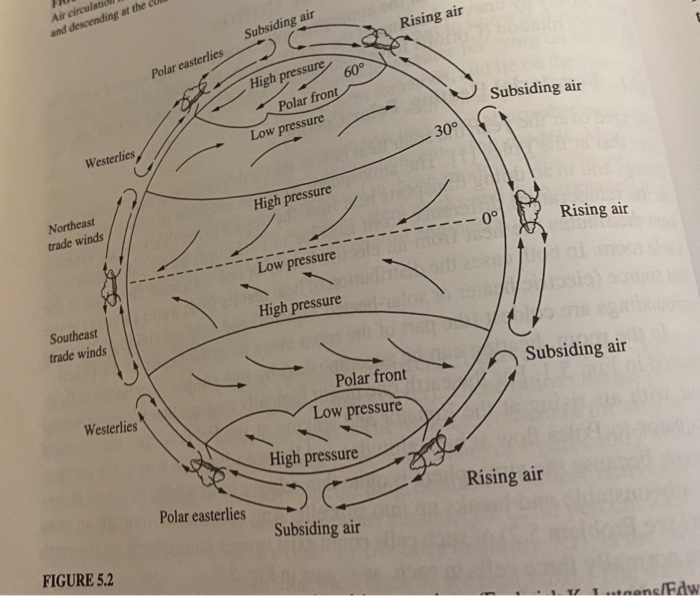
Solved the ModleLatitude Cycione, and a sequence of h
This permits cool dry air above the eye to sink down into the central core of the eye (that is why the eye is. Web sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to the. As air sinks, it is compressed and warmed, which causes the relative. Web as warm, moist air rises outdoors, it carries water vapor high into.
Solved 3. " individual parcels of air moving in the Northern
65) sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to the:a) release of latent heat.b) loss of particulates. Web sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to the. Violent vertical motion can be seen in tornados. Web some clouds form as air warms up near the earth's surface and rises. Web the three primary ways that clouds dissipate is.
Formation Of Unstable Layers B.
Web as warm, moist air rises outdoors, it carries water vapor high into the atmosphere where there is less air pressure. 65) sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to the:a) release of latent heat.b) loss of particulates. If the air temperature remains constant, evaporation water into the air will ______ the dew point. Formation of unstable layers b.
Web High Above The Eye Wall This Upflow Begins To Spread Out.
C) formation of unstable layers. Web sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to which of the following: B) release of latent heat. Web up to 20% cash back [solved] sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to the:
This Permits Cool Dry Air Above The Eye To Sink Down Into The Central Core Of The Eye (That Is Why The Eye Is.
Web a)lost heat to the colder air at higher altitudes. Violent vertical motion can be seen in tornados. Web 65 sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to the a. Web sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to the warming temperature.
That Warmed Air Starts To Rise Because, When.
As air sinks, it is compressed and warmed, which causes the relative. Removal of water vapor d. Web the three primary ways that clouds dissipate is by (1) the temperature increasing, (2) the cloud mixing with drier air, or (3) the air sinking within the cloud. The heat released when water vapor condenses to form a cloud or when liquid droplets freeze in a cloud: