Why Do Phospholipids Form A Bilayer In Water
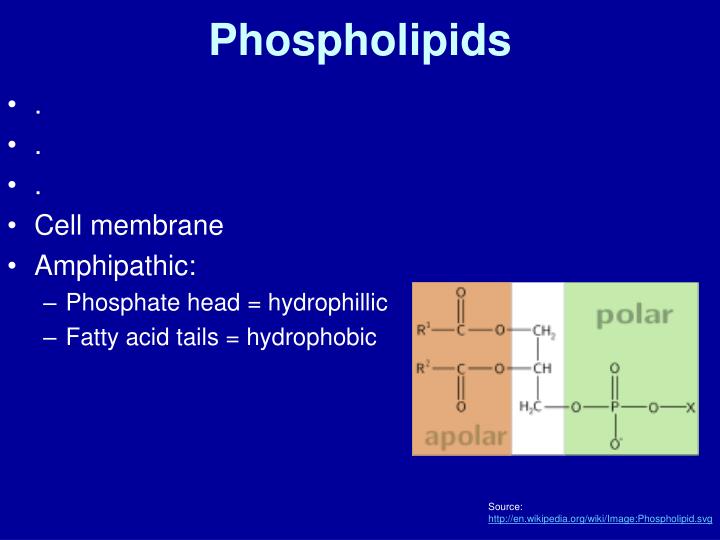
Why Do Phospholipids Form A Bilayer In Water - Lipid is known as amphipathic molecule because. So, it's not easy for water molecules to cross, and it is a somewhat slower process. Lipid is known as amphipathic molecule because. Why do phospholipids form bilayers in water? It comes in contact with water. Web phospholipids form a bilayer in water because lipid consists of hydrophillic and hydrophobic regions. Thus, the correct option for this question. But the phosphate group is hydrophilic, or soluble in water. In phospholipids, the two fatty acids are hydrophobic, or insoluble in water. The polar hydrophilic head group.
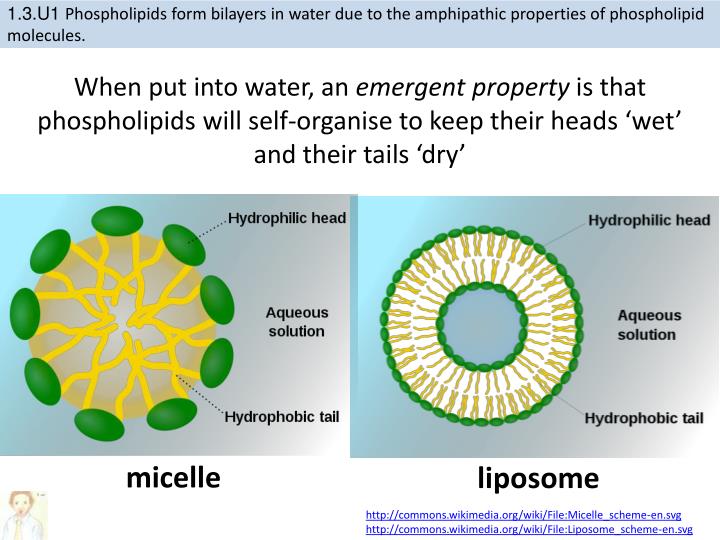
It comes in contact with water. Lipid is known as amphipathic molecule because. Phospholipids shape are cylindrical and the phospholipid molecules. In this cause water hating) tails and hydrophilic heads (water loving). So, it's not easy for water molecules to cross, and it is a somewhat slower process. In phospholipids, the two fatty acids are hydrophobic, or insoluble in water. Web the cell membrane consists of two adjacent layers of phospholipids, which form a bilayer. Web below are the reasons phospholipids form bilayers in water: The first clues to lipid bilayer structure came from results with red blood cell membranes. Phospholipids form a bilayer in water where the hydrophilic.
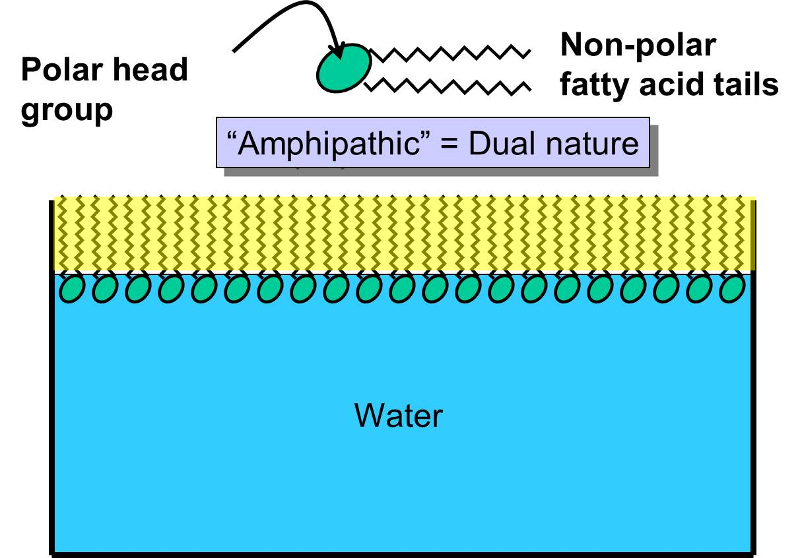
The fatty acid tails of phospholipids face inside, away from water, whereas the. It comes in contact with water. Web the cell membrane consists of two adjacent layers of phospholipids, which form a bilayer. Lipid is known as amphipathic molecule because. They cluster together and don't allow water. Web phospholipids form a bilayer in water because of the shape and amphipathic nature of the lipid molecules. The polar hydrophilic head group. Web phospholipids will form a bilayer in water because they contain hydrophobic (water fearing. Web when phospholipids are mixed with water, they form a phospholipid bilayer or double layer due to their amphipathic nature. Web biology questions and answers.
Phospholipid Definition, Structure, Function, Examples Science Terms
Phospholipids shape are cylindrical and the phospholipid molecules. Why do phospholipids form bilayers in water? It comes in contact with water. Web biology questions and answers. Web recall that the interior of the phospholipid bilayer is made up of the hydrophobic tails.
microbiology Why do cell membranes have a lipid bilayer instead of a
Lipid is known as amphipathic molecule because. The ultimate discovery that the plasma membrane is a lipid bilayer with. Why do phospholipids form bilayers in water? Web phospholipids form a bilayer in water because lipid consists of hydrophillic and hydrophobic regions. Web when phospholipids are mixed with water, they form a phospholipid bilayer or double layer due to their amphipathic.
PPT 1.3 Membrane Structure PowerPoint Presentation ID5735381
It comes in contact with water. Web below are the reasons phospholipids form bilayers in water: The first clues to lipid bilayer structure came from results with red blood cell membranes. Why do phospholipids form bilayers in water? Lipid is known as amphipathic molecule because.
Why Do Phospholipids Form A Bilayer In Water slidesharetrick
O they have a hydrophilic head that interacts with water and hydrophobic tails that arrange. Thus, the correct option for this question. The first clues to lipid bilayer structure came from results with red blood cell membranes. Web recall that the interior of the phospholipid bilayer is made up of the hydrophobic tails. Lipid is known as amphipathic molecule because.
A phospholipid
They cluster together and don't allow water. Web biology questions and answers. The first clues to lipid bilayer structure came from results with red blood cell membranes. A) because they are amphipathic molecules (polar and hydrophobic regions on the same. Web phospholipids form a bilayer in water because the phosphate portions attract water, and the lipid portions repel water.
PPT Lipids PowerPoint Presentation ID7034255
Web biology questions and answers. Web phospholipids form a bilayer in water because the phosphate portions attract water, and the lipid portions repel water. It comes in contact with water. Web the cell membrane consists of two adjacent layers of phospholipids, which form a bilayer. So, it's not easy for water molecules to cross, and it is a somewhat slower.
Components and Structure OpenStax Biology 2e
Web recall that the interior of the phospholipid bilayer is made up of the hydrophobic tails. The polar hydrophilic head group. O they have a hydrophilic head that interacts with water and hydrophobic tails that arrange. Web phospholipids form a bilayer in water because of the shape and amphipathic nature of the lipid molecules. In phospholipids, the two fatty acids.
Why Do Phospholipids Form A Bilayer In Water?
The first clues to lipid bilayer structure came from results with red blood cell membranes. Web phospholipids form a bilayer in water because lipid consists of hydrophillic and hydrophobic regions. In phospholipids, the two fatty acids are hydrophobic, or insoluble in water. Web the cell membrane consists of two adjacent layers of phospholipids, which form a bilayer. O they have.
Why do phospholipids form a bilayer in water? Brainly.in
O they have a hydrophilic head that interacts with water and hydrophobic tails that arrange. Lipid is known as amphipathic molecule because. In phospholipids, the two fatty acids are hydrophobic, or insoluble in water. Web phospholipids form a bilayer in water because of the shape and amphipathic nature of the lipid molecules. Web below are the reasons phospholipids form bilayers.
Why Do Phospholipids Form A Bilayer In Water slidesharetrick
Why do phospholipids form bilayers in water? O they have a hydrophilic head that interacts with water and hydrophobic tails that arrange. They cluster together and don't allow water. Phospholipids shape are cylindrical and the phospholipid molecules. Web below are the reasons phospholipids form bilayers in water:
The Fatty Acid Tails Of Phospholipids Face Inside, Away From Water, Whereas The.
A) because they are amphipathic molecules (polar and hydrophobic regions on the same. Web phospholipids form a bilayer in water because of the shape and amphipathic nature of the lipid molecules. Why do phospholipids form bilayers in water? So, it's not easy for water molecules to cross, and it is a somewhat slower process.
Web Biology Questions And Answers.
O they have a hydrophilic head that interacts with water and hydrophobic tails that arrange. It comes in contact with water. Web phospholipids form a bilayer in water because lipid consists of hydrophillic and hydrophobic regions. Why do phospholipids form bilayers in water?
Web Recall That The Interior Of The Phospholipid Bilayer Is Made Up Of The Hydrophobic Tails.
Web phospholipids form a bilayer in water because lipid consists of hydrophillic and hydrophobic regions. Web phospholipids form a bilayer in water because the phosphate portions attract water, and the lipid portions repel water. The polar hydrophilic head group. Thus, the correct option for this question.
Lipid Is Known As Amphipathic Molecule Because.
Web below are the reasons phospholipids form bilayers in water: But the phosphate group is hydrophilic, or soluble in water. Web phospholipids will form a bilayer in water because they contain hydrophobic (water fearing. The first clues to lipid bilayer structure came from results with red blood cell membranes.



.PNG)