What Three Elements Are Used To Form Sugar Molecules
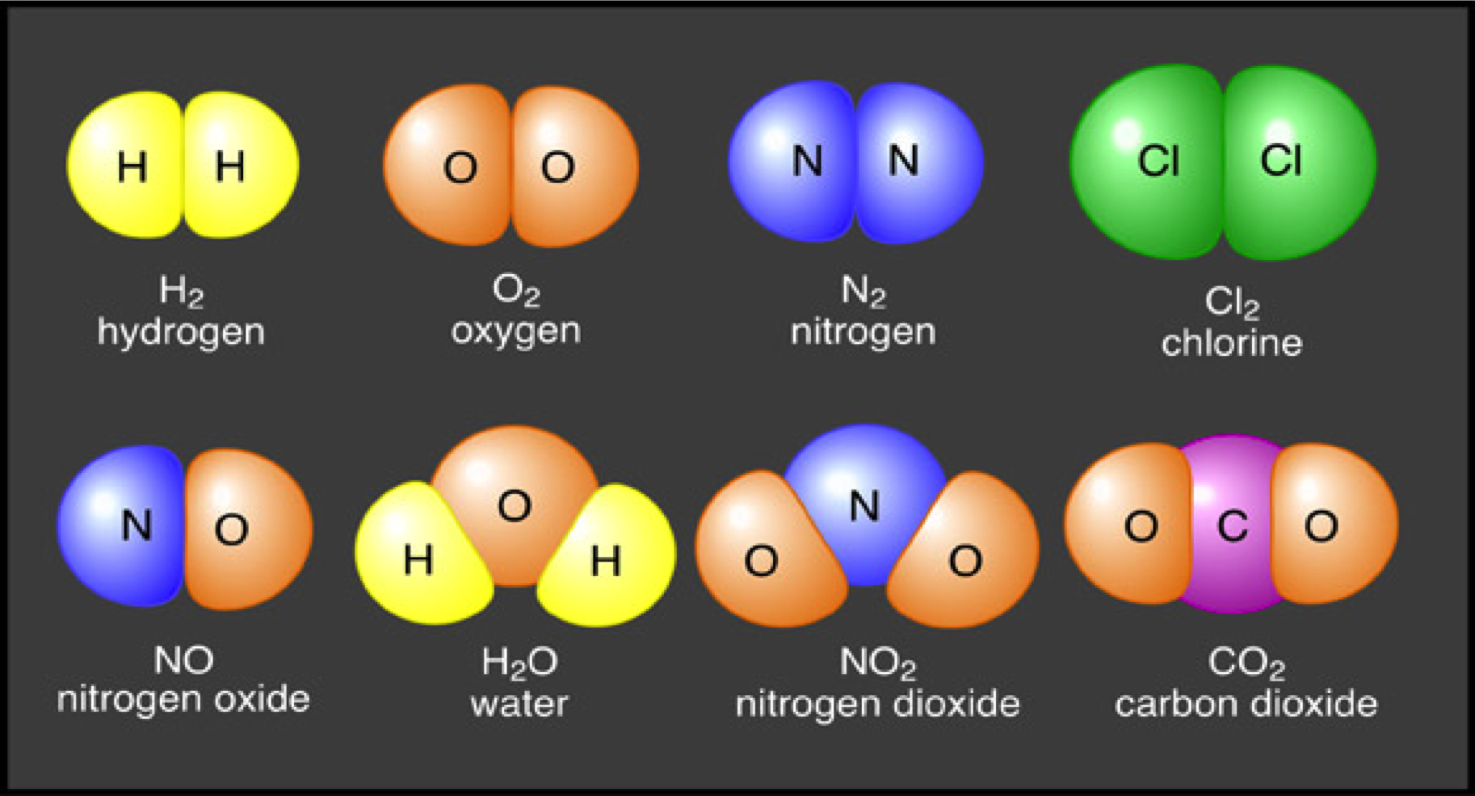
What Three Elements Are Used To Form Sugar Molecules - For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined from either sugarcane or sugar beet. Dextrose ( glucose) is the major monosaccharide. This is the same reason that fructose is sweet. Web in the dehydration synthesis reaction above, two molecules of the sugar glucose (monomers) combine to form a single molecule of the sugar maltose. While sugar qualitatively resembles table salt (often confused in the kitchen), the two have distinctly different physical and chemical properties. Web what three elements are in all carbohydrates including sugar? Web science & technology what elements make up sugar? It's the way these atoms are connected that makes each type of carbohydrate different. Sucrose (common sugar) is the primary example of a disaccharide. Web sugar molecules contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen:
12 carbon atoms, 22 hydrogen atoms, and 11 oxygen atoms. Web as a chemical term, “sugar” usually refers to all carbohydrates of the general formula c n (h 2 o) n. Web science & technology what elements make up sugar? All carbohydrates, like sucrose, must have a 2:1 ratio of hydrogens to oxygen. Dextrose ( glucose) is the major monosaccharide. Its chemical formula is c12h22o11, and it contains carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. The black stuff is called burnt sugar! Web the molecular structure of sugar (sucrose) is c12h22o11. Other forms of sugar, like glucose,. Web 1 comment ( 85 votes) upvote flag quantum coding 4 years ago glucose is sweet because it contains oh groups with a certain orientation that interacts with the taste receptor for sweetness in our tongues.
Web in the dehydration synthesis reaction above, two molecules of the sugar glucose (monomers) combine to form a single molecule of the sugar maltose. While sugar qualitatively resembles table salt (often confused in the kitchen), the two have distinctly different physical and chemical properties. Sugars are thus all aldehydes and ketones and are usually referred to as aldoses or ketoses. In sucrose, there are 22 hydrogens and 11 oxygens. The four nucleobases in dna are guanine, adenine, cytosine and thymine; Most table sugar comes from sugar beets or. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. This is the same reason that fructose is sweet. Sucrose (common sugar) is the primary example of a disaccharide. It’s found naturally in most plants, but especially in sugarcane and sugar beets—hence their names.
Biocanvas The addition of tiny sugar molecules onto proteins...
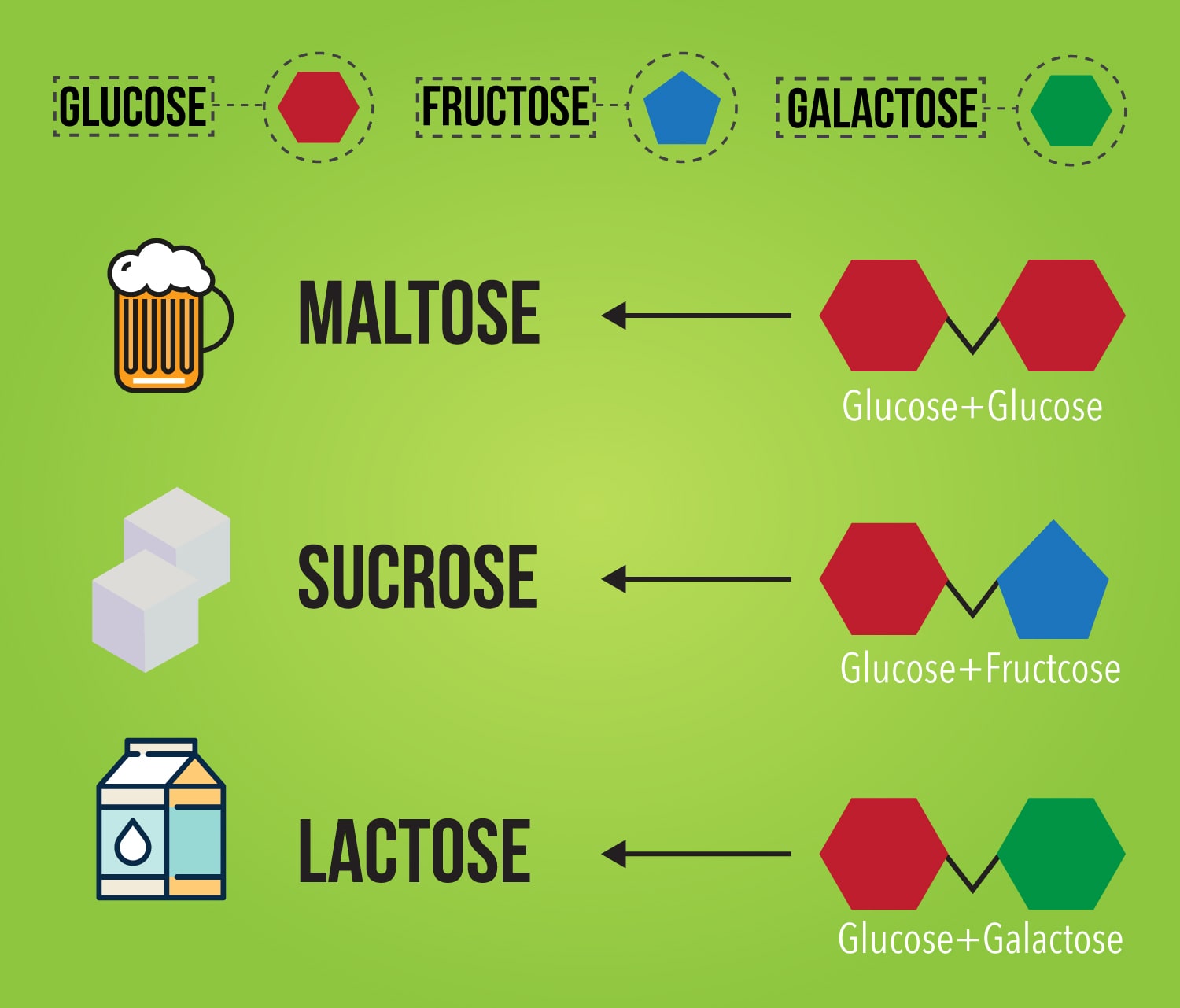
Web compound sugars, also called or double sugars, are molecules made of two monosaccharides; Web in the dehydration synthesis reaction above, two molecules of the sugar glucose (monomers) combine to form a single molecule of the sugar maltose. Web sugar is made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. The name carbohydrate reveals the chemical make up of this nutrient.
Carbon — Role and Importance to Life Expii
Web as a chemical term, “sugar” usually refers to all carbohydrates of the general formula c n (h 2 o) n. One of the glucose molecules loses an h, the other loses an oh group, and a water molecule is released as a new covalent bond forms between the two glucose molecules. While sugar qualitatively resembles table salt (often confused.
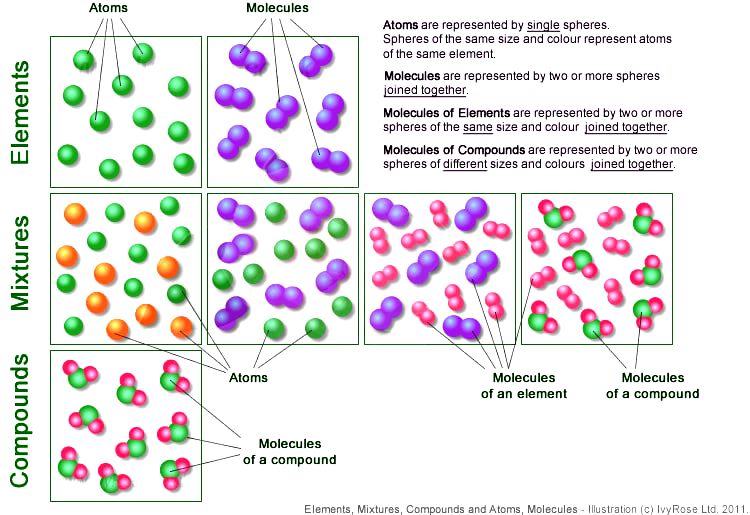
1B3 Atoms and Molecules
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined from either sugarcane or sugar beet. In the body, compound sugars are Web these groups are the following: Web what three elements are in all carbohydrates including sugar? 12 carbon atoms, 22 hydrogen atoms, and 11 oxygen atoms.
[LS16] Sugar to Carbon Molecules Biology Dictionary
The type of sugar called sucrose is also known as saccharose. Examples are starches, dextrins, and. Web 1 comment ( 85 votes) upvote flag quantum coding 4 years ago glucose is sweet because it contains oh groups with a certain orientation that interacts with the taste receptor for sweetness in our tongues. Other forms of sugar, like glucose,. For human.
Complex sugar molecules may be the key to safer chemo
Web the white stuff we know as sugar is sucrose, a molecule composed of 12 atoms of carbon, 22 atoms of hydrogen, and 11 atoms of oxygen (c12h22o11). Web what 3 elements can be used to make sugar molecules? More specifically, each molecule of sugar has 12 carbon atoms, 22 hydrogen atoms and 11 oxygen atoms. The name carbohydrate reveals.
Molecule Clipart Simple Sugar Molecules Png Download (409596
Web the white stuff we know as sugar is sucrose, a molecule composed of 12 atoms of carbon, 22 atoms of hydrogen, and 11 atoms of oxygen (c12h22o11). Web there are several different types of sugar, but generally when one asks for the molecular formula of sugar, the question refers to table sugar or sucrose. Web in the dehydration synthesis.
Mr. Villa's Science Stars! Elements vs Compounds, and Atoms too
Web sugar has the chemical formulate \ (\ce {c12h22o11}\) and is constructed from different elements than salt: One of the glucose molecules loses an h, the other loses an oh group, and a water molecule is released as a new covalent bond forms between the two glucose molecules. Most table sugar comes from sugar beets or. Web sucrose sucrose, a.
How sugar molecules secretly shaped human evolution
Web science & technology what elements make up sugar? Web the white stuff we know as sugar is sucrose, a molecule composed of 12 atoms of carbon, 22 atoms of hydrogen, and 11 atoms of oxygen (c12h22o11). Web table sugar, or sucrose, is a compound because it’s formed when two or more elements are joined together. It is produced naturally.
CH150 Chapter 4 Covalent Bonds and Molecular Compounds Chemistry
Web as a chemical term, “sugar” usually refers to all carbohydrates of the general formula c n (h 2 o) n. Web what three elements are in all carbohydrates including sugar? The four nucleobases in dna are guanine, adenine, cytosine and thymine; The name carbohydrate reveals the chemical make up of this nutrient class. Web the molecular structure of sugar.
SugarMoleculesSynthesis Dr. Sarah Larsen Medical Intuitive and
Web there are several different types of sugar, but generally when one asks for the molecular formula of sugar, the question refers to table sugar or sucrose. This is the same reason that fructose is sweet. Web the molecular structure of sugar (sucrose) is c12h22o11. Sucrose is a disaccharide, or double sugar, being composed of one molecule of glucose linked.
Web The Chemical Or Molecular Formula For Sucrose Is C12H22O11, Which Means Each Molecule Of Sugar Contains 12 Carbon Atoms, 22 Hydrogen Atoms And 11 Oxygen Atoms.
Web sucrose sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. Its chemical formula is c12h22o11, and it contains carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. This is the same reason that fructose is sweet. Web the white stuff we know as sugar is sucrose, a molecule composed of 12 atoms of carbon, 22 atoms of hydrogen, and 11 atoms of oxygen (c12h22o11).
Web Table Sugar, Or Sucrose, Is A Compound Because It’s Formed When Two Or More Elements Are Joined Together.
A molecule like glucose is called an alde hex ose since it contains six carbon atoms. Web compound sugars, also called or double sugars, are molecules made of two monosaccharides; Web chemical education digital library (chemed dl). 12 carbon atoms, 22 hydrogen atoms, and 11 oxygen atoms.
In Rna, Uracil Is Used In Place Of Thymine.
Web as a chemical term, “sugar” usually refers to all carbohydrates of the general formula c n (h 2 o) n. While sugar qualitatively resembles table salt (often confused in the kitchen), the two have distinctly different physical and chemical properties. It’s found naturally in most plants, but especially in sugarcane and sugar beets—hence their names. More specifically, each molecule of sugar has 12 carbon atoms, 22 hydrogen atoms and 11 oxygen atoms.
All Carbohydrates, Like Sucrose, Must Have A 2:1 Ratio Of Hydrogens To Oxygen.
Sucrose is a disaccharide, or double sugar, being composed of one molecule of glucose linked to one molecule of fructose. Web in the dehydration synthesis reaction above, two molecules of the sugar glucose (monomers) combine to form a single molecule of the sugar maltose. Dextrose ( glucose) is the major monosaccharide. The difference between different sugars can be very subtle.


![[LS16] Sugar to Carbon Molecules Biology Dictionary](https://biologydictionary.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/Common-amino-acids.jpg)