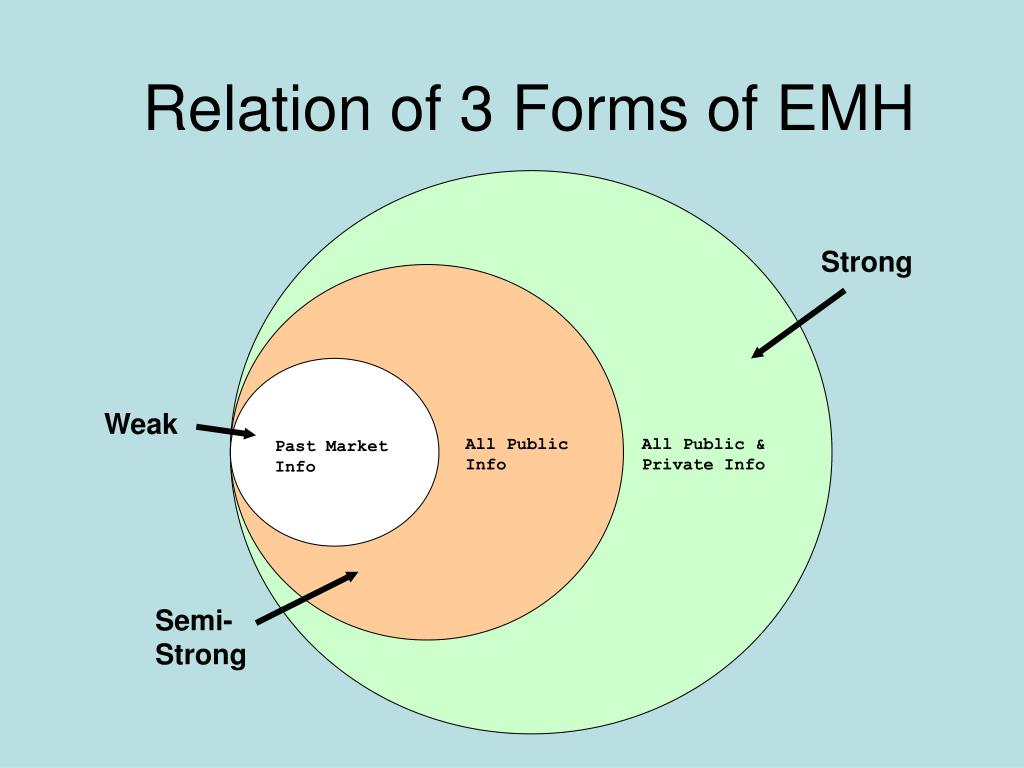
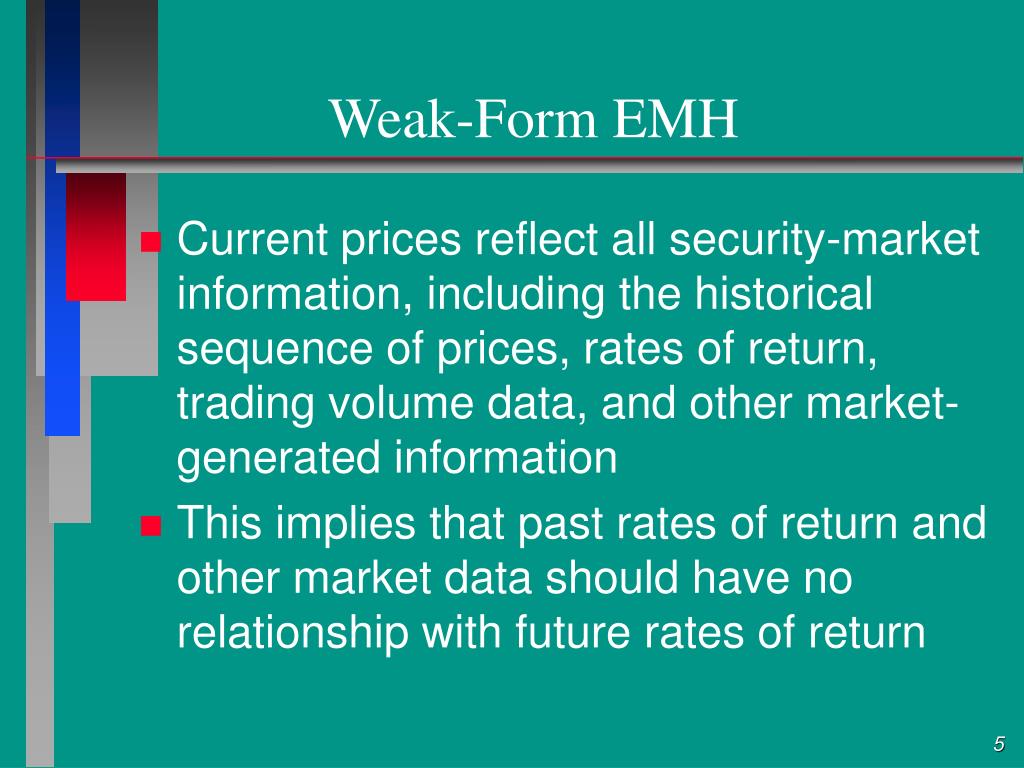
Weak Form Emh
Weak Form Emh - Web weak form efficiency is one of the three different degrees of efficient market hypothesis (emh). Key takeaways weak form efficiency states that past prices, historical values, and. The efficient market hypothesis concerns the extent to which outside information has an effect upon the market price of a security. Fundamental analysis of securities can provide you with information to produce returns above market averages in the short term. Web the market capitalization of emerging market economies accounts for twelve percent of world market capitalization and has more than doubled, growing from less than $2 trillion in 1995 to $5 trillion in 2006 (nally, 2010). All public and private information, inclusive of insider information, is reflected in market prices. Web weak form market efficiency, also known as he random walk theory is part of the efficient market hypothesis. Web the efficient market hypothesis (emh), as a whole, theorizes that the market is generally efficient, but the theory is offered in three different versions: Weak form emh suggests that all past information is priced into securities. The weak form of the emh assumes that the prices of securities reflect all available public market information but may not reflect new information that is not yet publicly available.
There are three beliefs or views: All publicly available information is reflected in the current market prices. Web weak form emh: It additionally assumes that past information regarding price, volume, and returns is independent of future prices. Web the market capitalization of emerging market economies accounts for twelve percent of world market capitalization and has more than doubled, growing from less than $2 trillion in 1995 to $5 trillion in 2006 (nally, 2010). All public and private information, inclusive of insider information, is reflected in market prices. All past information like historical trading prices and volume data is reflected in the market prices. Web weak form market efficiency, also known as he random walk theory is part of the efficient market hypothesis. Web weak form efficiency is one of the three different degrees of efficient market hypothesis (emh). Fundamental analysis of securities can provide you with information to produce returns above market averages in the short term.
Web weak form market efficiency, also known as he random walk theory is part of the efficient market hypothesis. The weak form of market efficiency is the weakest form of this hypothesis model. Web the efficient market hypothesis (emh), as a whole, theorizes that the market is generally efficient, but the theory is offered in three different versions: Weak form emh suggests that all past information is priced into securities. All publicly available information is reflected in the current market prices. Web weak form efficiency is one of the three different degrees of efficient market hypothesis (emh). It additionally assumes that past information regarding price, volume, and returns is independent of future prices. Key takeaways weak form efficiency states that past prices, historical values, and. All past information like historical trading prices and volume data is reflected in the market prices. The weak form of the emh assumes that the prices of securities reflect all available public market information but may not reflect new information that is not yet publicly available.
PPT Market Efficiency and Empirical Evidence PowerPoint Presentation
Web weak form market efficiency, also known as he random walk theory is part of the efficient market hypothesis. Web weak form emh: Weak form emh suggests that all past information is priced into securities. Fundamental analysis of securities can provide you with information to produce returns above market averages in the short term. Web the market capitalization of emerging.
PPT Chapter 10 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID395356
Web weak form efficiency is one of the three different degrees of efficient market hypothesis (emh). The efficient market hypothesis concerns the extent to which outside information has an effect upon the market price of a security. Weak form emh suggests that all past information is priced into securities. Key takeaways weak form efficiency states that past prices, historical values,.
Weak Form of EMH (T39) YouTube
The weak form of market efficiency is the weakest form of this hypothesis model. It additionally assumes that past information regarding price, volume, and returns is independent of future prices. Web weak form market efficiency, also known as he random walk theory is part of the efficient market hypothesis. Weak form emh suggests that all past information is priced into.
What does Warren Buffett tell me about EMH on his winning bet?
The weak form of market efficiency is the weakest form of this hypothesis model. The efficient market hypothesis concerns the extent to which outside information has an effect upon the market price of a security. Fundamental analysis of securities can provide you with information to produce returns above market averages in the short term. Key takeaways weak form efficiency states.
Efficient market hypothesis
It additionally assumes that past information regarding price, volume, and returns is independent of future prices. The weak form of the emh assumes that the prices of securities reflect all available public market information but may not reflect new information that is not yet publicly available. Key takeaways weak form efficiency states that past prices, historical values, and. The efficient.
Efficient market hypothesis
Web the efficient market hypothesis (emh), as a whole, theorizes that the market is generally efficient, but the theory is offered in three different versions: All publicly available information is reflected in the current market prices. Web weak form emh: Key takeaways weak form efficiency states that past prices, historical values, and. The weak form of market efficiency is the.
CHAPTER 8 Stocks and Their Valuation n n
Weak form emh suggests that all past information is priced into securities. All past information like historical trading prices and volume data is reflected in the market prices. All public and private information, inclusive of insider information, is reflected in market prices. Web weak form emh: Web weak form efficiency is one of the three different degrees of efficient market.
What is the Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH)? IG Bank Switzerland
The weak form of the emh assumes that the prices of securities reflect all available public market information but may not reflect new information that is not yet publicly available. Weak form emh suggests that all past information is priced into securities. Key takeaways weak form efficiency states that past prices, historical values, and. All past information like historical trading.
Weak form efficiency indian stock markets make money with meghan system
All publicly available information is reflected in the current market prices. Web the efficient market hypothesis (emh), as a whole, theorizes that the market is generally efficient, but the theory is offered in three different versions: All past information like historical trading prices and volume data is reflected in the market prices. Web weak form emh: Web weak form market.
PPT Efficient Market Theory PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Fundamental analysis of securities can provide you with information to produce returns above market averages in the short term. All publicly available information is reflected in the current market prices. Weak form emh suggests that all past information is priced into securities. All past information like historical trading prices and volume data is reflected in the market prices. The weak.
The Weak Form Of Market Efficiency Is The Weakest Form Of This Hypothesis Model.
There are three beliefs or views: The efficient market hypothesis concerns the extent to which outside information has an effect upon the market price of a security. Web the market capitalization of emerging market economies accounts for twelve percent of world market capitalization and has more than doubled, growing from less than $2 trillion in 1995 to $5 trillion in 2006 (nally, 2010). Web the efficient market hypothesis (emh), as a whole, theorizes that the market is generally efficient, but the theory is offered in three different versions:
All Publicly Available Information Is Reflected In The Current Market Prices.
All public and private information, inclusive of insider information, is reflected in market prices. Fundamental analysis of securities can provide you with information to produce returns above market averages in the short term. Web weak form market efficiency, also known as he random walk theory is part of the efficient market hypothesis. All past information like historical trading prices and volume data is reflected in the market prices.
The Weak Form Of The Emh Assumes That The Prices Of Securities Reflect All Available Public Market Information But May Not Reflect New Information That Is Not Yet Publicly Available.
Web weak form emh: It additionally assumes that past information regarding price, volume, and returns is independent of future prices. Web weak form efficiency is one of the three different degrees of efficient market hypothesis (emh). Weak form emh suggests that all past information is priced into securities.