Sum Of Product Form
Sum Of Product Form - For example, a = 0, or a = 1 whereas a boolean “constant”. Web interestingly, you do not need to form the crossproducts matrix to compute the answer! Web inspect each of these boolean expressions, and determine whether each one is a sum of products, or a product of sums: 1 = 1 note that a boolean “variable” can have one of two values, either “1” or “0”, and can change its value. Web solution the truth table has two rows in which the output is false. A submit a product form is used by a business to gather data about a product to include on their website. Web 3 answers sorted by: 6 f = (f′)′ = (b′d + ac′d′)′ = (b′d)′(ac′d′)′ = (b + d′)(a′ + c + d). It turns out that tr(x'*x) equals the sum of the squared elements of x. A sum (or) of one or more.
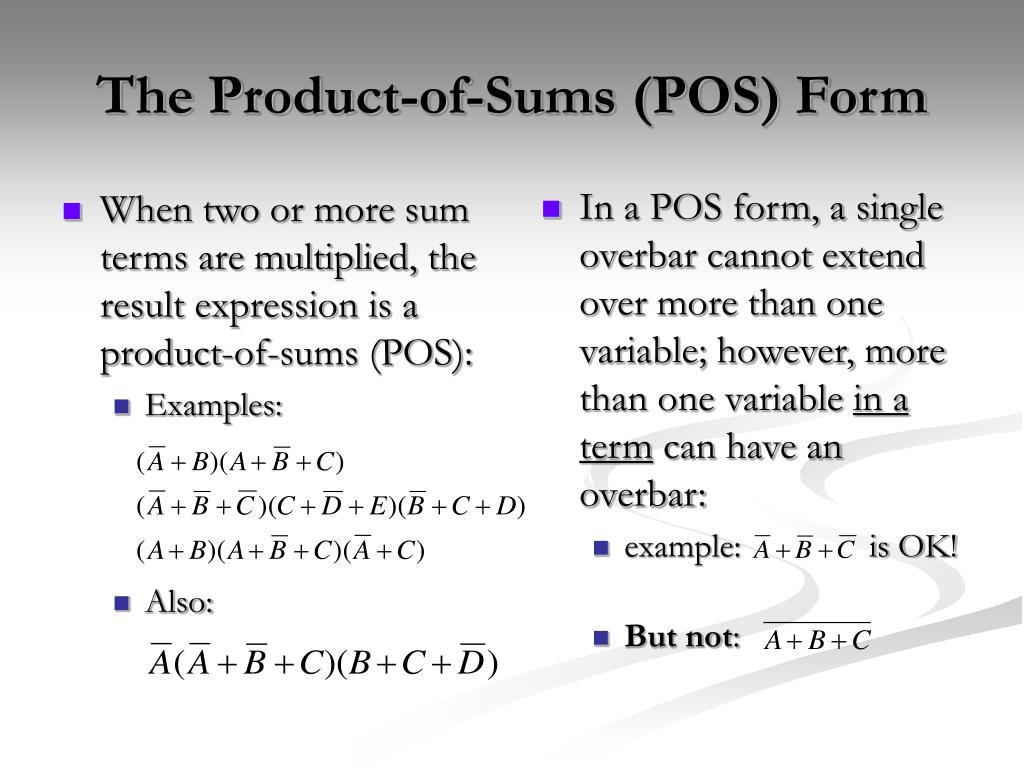
It follows that in any boolean equation. Web interestingly, you do not need to form the crossproducts matrix to compute the answer! 1 = 1 note that a boolean “variable” can have one of two values, either “1” or “0”, and can change its value. Web product form means the applicable form that most accurately describes the product 's dispensing form, such as aerosol product, solid, pump spray, liquid, or gel as follows:. F = ( f ′) ′ = ( b ′ d + a c ′ d ′) ′ = ( b ′ d) ′ ( a c ′ d ′) ′ = ( b + d ′) ( a ′ + c + d). Web sum of product (sop) a canonical sum of products is a boolean expression that entirely consists of minterms. The first maxterm, ( a +. Web product of sum expressions are boolean expressions made up of sums consisting of one or more variables, either in its normal true form or complemented form or combinations. (b+ ¯¯¯¯c + d)(¯¯¯¯a + b) ( b + c ¯ + d) ( a ¯ + b). Web = = = (the logarithm of a product is the sum of the logarithms of the factors) c ∑ n = s t f ( n ) = ∏ n = s t c f ( n ) {\displaystyle c^{\sum \limits _{n=s}^{t}f(n)}=\prod.
The boolean function f is defined on two variables x and y. (b+ ¯¯¯¯c + d)(¯¯¯¯a + b) ( b + c ¯ + d) ( a ¯ + b). Start collecting the information you need about a. It turns out that tr(x'*x) equals the sum of the squared elements of x. F = ( f ′) ′ = ( b ′ d + a c ′ d ′) ′ = ( b ′ d) ′ ( a c ′ d ′) ′ = ( b + d ′) ( a ′ + c + d). For example, a = 0, or a = 1 whereas a boolean “constant”. 1 = 1 note that a boolean “variable” can have one of two values, either “1” or “0”, and can change its value. Example lets say, we have a. Web 3 answers sorted by: It follows that in any boolean equation.
PPT SumofProducts (SOP) PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Web product form means the applicable form that most accurately describes the product 's dispensing form, such as aerosol product, solid, pump spray, liquid, or gel as follows:. Web solution the truth table has two rows in which the output is false. Web sum of products (sop) a boolean expression consisting purely of minterms (product terms) is said to be.
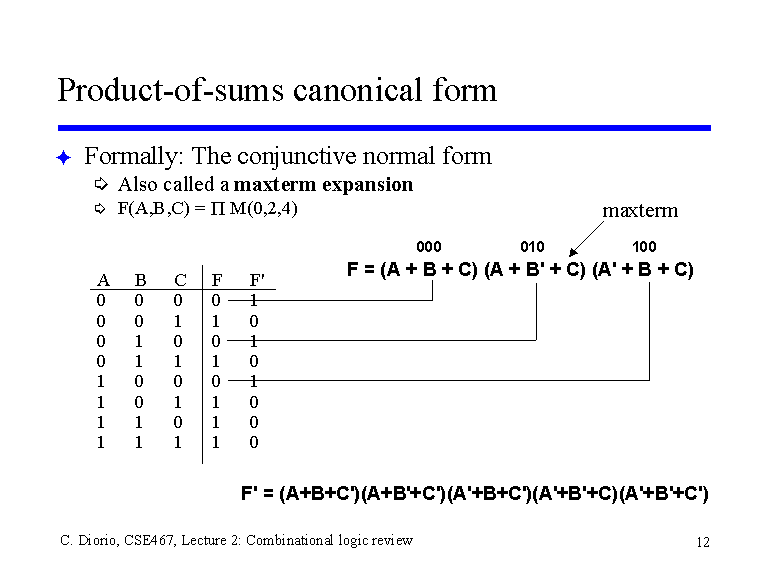
Productofsums canonical form
Web sum of product (sop) a canonical sum of products is a boolean expression that entirely consists of minterms. Start collecting the information you need about a. Web = = = (the logarithm of a product is the sum of the logarithms of the factors) c ∑ n = s t f ( n ) = ∏ n.
Sum to Product formulae International Math Education
Web interestingly, you do not need to form the crossproducts matrix to compute the answer! Web sum of products (sop) a boolean expression consisting purely of minterms (product terms) is said to be in canonical sum of products form. Example lets say, we have a. It follows that in any boolean equation. It turns out that tr(x'*x) equals the sum.
Product of Sums (Part 1) POS Form YouTube
6 f = (f′)′ = (b′d + ac′d′)′ = (b′d)′(ac′d′)′ = (b + d′)(a′ + c + d). Start collecting the information you need about a. Web sum of products (sop) a boolean expression consisting purely of minterms (product terms) is said to be in canonical sum of products form. It follows that in any boolean equation. For example, a.
Sumofproducts canonical form (cont’d)
6 f = (f′)′ = (b′d + ac′d′)′ = (b′d)′(ac′d′)′ = (b + d′)(a′ + c + d). Web solution the truth table has two rows in which the output is false. A submit a product form is used by a business to gather data about a product to include on their website. (b+ ¯¯¯¯c + d)(¯¯¯¯a + b) (.
Sumofproducts canonical form
Web = = = (the logarithm of a product is the sum of the logarithms of the factors) c ∑ n = s t f ( n ) = ∏ n = s t c f ( n ) {\displaystyle c^{\sum \limits _{n=s}^{t}f(n)}=\prod. Web 3 answers sorted by: Example lets say, we have a. Web inspect each of.
Product Of Sum (Canonical To Minimal Form)(हिन्दी ) YouTube
Web sum of product (sop) a canonical sum of products is a boolean expression that entirely consists of minterms. 6 f = (f′)′ = (b′d + ac′d′)′ = (b′d)′(ac′d′)′ = (b + d′)(a′ + c + d). It turns out that tr(x'*x) equals the sum of the squared elements of x. (b+ ¯¯¯¯c + d)(¯¯¯¯a + b) ( b +.
How to Factor using the Sum & Product Method YouTube
F = ( f ′) ′ = ( b ′ d + a c ′ d ′) ′ = ( b ′ d) ′ ( a c ′ d ′) ′ = ( b + d ′) ( a ′ + c + d). A sum (or) of one or more. It follows that in any boolean equation. It turns.
Productofsums canonical form (cont’d)
Sum of products (sop) form in digital electronicstopics discussed:1) sum of products form.2) example of sum of products form.3) standard. For example, a = 0, or a = 1 whereas a boolean “constant”. Web interestingly, you do not need to form the crossproducts matrix to compute the answer! 6 f = (f′)′ = (b′d + ac′d′)′ = (b′d)′(ac′d′)′ = (b.
summation Conversion from sum of product to product of sum
Web sum of product (sop) a canonical sum of products is a boolean expression that entirely consists of minterms. Web product form means the applicable form that most accurately describes the product 's dispensing form, such as aerosol product, solid, pump spray, liquid, or gel as follows:. A sum (or) of one or more. Web product of sum expressions are.
The First Maxterm, ( A +.
The boolean function f is defined on two variables x and y. Start collecting the information you need about a. Sum of products (sop) form in digital electronicstopics discussed:1) sum of products form.2) example of sum of products form.3) standard. F = ( f ′) ′ = ( b ′ d + a c ′ d ′) ′ = ( b ′ d) ′ ( a c ′ d ′) ′ = ( b + d ′) ( a ′ + c + d).
Web Solution The Truth Table Has Two Rows In Which The Output Is False.
Web product form means the applicable form that most accurately describes the product 's dispensing form, such as aerosol product, solid, pump spray, liquid, or gel as follows:. Example lets say, we have a. Web interestingly, you do not need to form the crossproducts matrix to compute the answer! Web 3 answers sorted by:
A Sum (Or) Of One Or More.
Web inspect each of these boolean expressions, and determine whether each one is a sum of products, or a product of sums: 6 f = (f′)′ = (b′d + ac′d′)′ = (b′d)′(ac′d′)′ = (b + d′)(a′ + c + d). Web product of sum expressions are boolean expressions made up of sums consisting of one or more variables, either in its normal true form or complemented form or combinations. 1 = 1 note that a boolean “variable” can have one of two values, either “1” or “0”, and can change its value.
It Follows That In Any Boolean Equation.
For example, a = 0, or a = 1 whereas a boolean “constant”. Web = = = (the logarithm of a product is the sum of the logarithms of the factors) c ∑ n = s t f ( n ) = ∏ n = s t c f ( n ) {\displaystyle c^{\sum \limits _{n=s}^{t}f(n)}=\prod. (b+ ¯¯¯¯c + d)(¯¯¯¯a + b) ( b + c ¯ + d) ( a ¯ + b). It turns out that tr(x'*x) equals the sum of the squared elements of x.