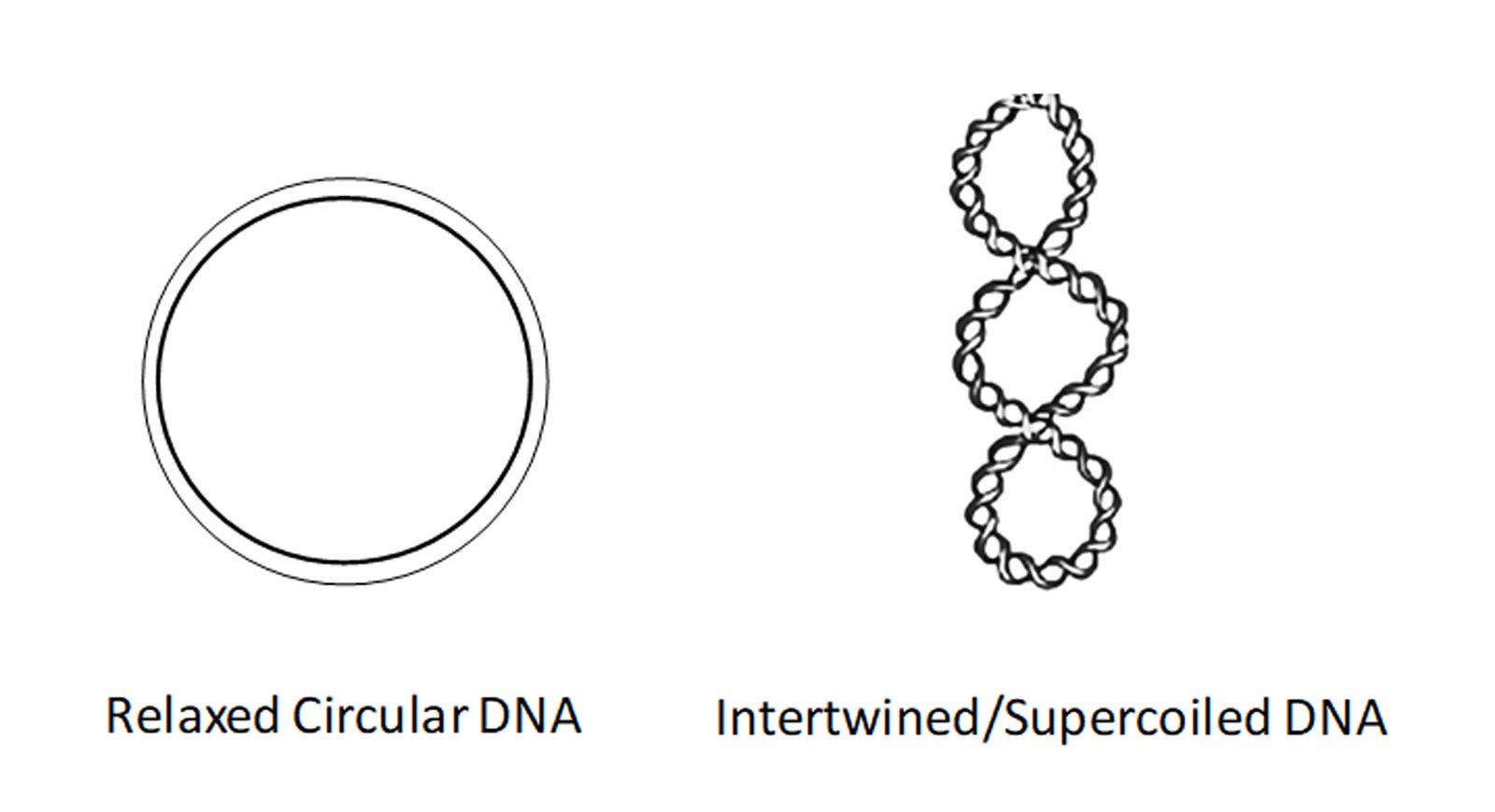
Relaxed Form Of Dna
Relaxed Form Of Dna - Deoxy means lack of an oxygen atom, ribo means ribose sugar, nucleic is found in the nucleus of cell and acid. The life of a cell, how it grows and divides. Web if such a relaxed dna circle with a nick was ligated, it would have the highest chance to form a dna topoisomer having an lk = 76. Web what is relaxed dna? Web higher molecular weight forms of the plasmid can also sometimes be seen, including a nicked or relaxed form, referred to as open circular, which typically migrates. Web supercoiled state corresponds to the active form for plasmid applications. Circular dna that is not supercoiled (see supercoil), and instead has an unwound loop. Web the dna full form is deoxyribonucleic acid. Web a‑form nucleic acids and z‑dna. The relaxed structure on the left is not found unless the chromosome is nicked;
A phase of mitosis in which chromosomes become visible and nuclear membrane disappears. The supercoiled form is energetically favoured over the. Web what is relaxed dna? Web interestingly, dna in its relaxed form barely moved. Web catch the top stories of the day on anc’s ‘top story’ (28 july 2023) Circular dna that is not supercoiled (see supercoil), and instead has an unwound loop. Web supercoiled state corresponds to the active form for plasmid applications. Cell cycle is made of 3 parts: Circular dna that is not supercoiled (see supercoil), and instead has an unwound loop. Deoxy means lack of an oxygen atom, ribo means ribose sugar, nucleic is found in the nucleus of cell and acid.
Circular dna that is not supercoiled (see supercoil), and instead has an unwound loop. Web catch the top stories of the day on anc’s ‘top story’ (28 july 2023) Web interestingly, dna in its relaxed form barely moved. Dna is a set of molecules responsible for the transmitting and carrying the inherited materials or genetic instructions from parents to. Web the relaxed form of dna in the cell's nucleus. The supercoiled form is energetically favoured over the. Relaxed, uncoiled, unorganized form of dna,. Cell cycle is made of 3 parts: Three different forms of duplex nucleic acid have been described. Circular dna that is not supercoiled (see supercoil), and instead has an unwound loop.
eXe
Access to the complete content on oxford. Web interestingly, dna in its relaxed form barely moved. What happens when dna is relaxed?. Web supercoiled state corresponds to the active form for plasmid applications. Circular dna that is not supercoiled (see supercoil), and instead has an unwound loop.
DNA supercoils in chromatin. a Twist and writhe in naked DNA. Twist is
Web supercoiled state corresponds to the active form for plasmid applications. But when twisted — as it normally does when squeezing into a cell — the dna morphed into many other. The most common form, present in most dna at neutral ph and. Cell cycle is made of 3 parts: Web a‑form nucleic acids and z‑dna.
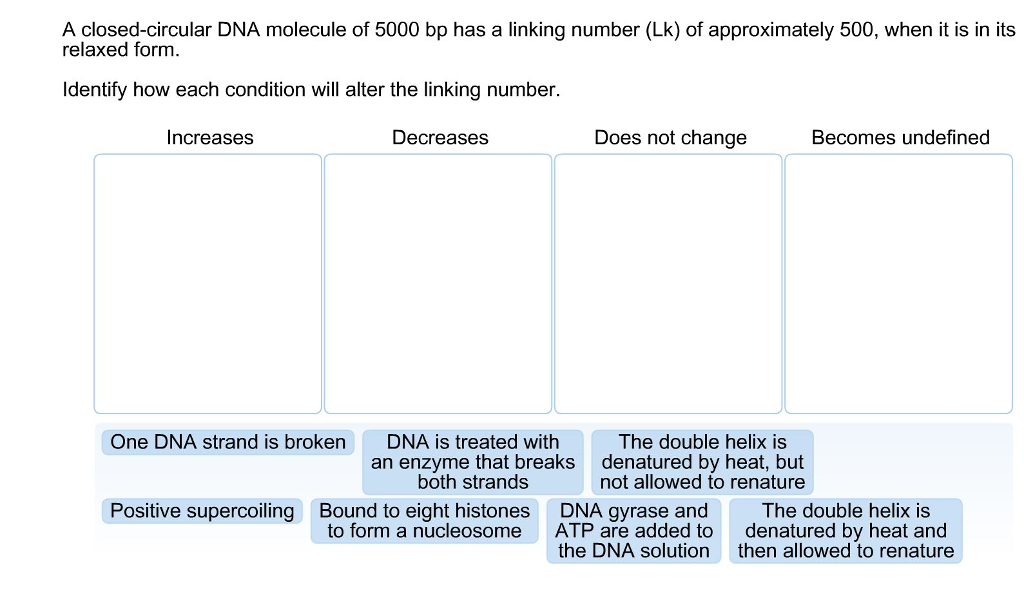
Solved A closedcircular DNA molecule of 5000 bp has a
Deoxy means lack of an oxygen atom, ribo means ribose sugar, nucleic is found in the nucleus of cell and acid. Web the full form of dna is deoxyribonucleic acid. Web supercoiled state corresponds to the active form for plasmid applications. Web a‑form nucleic acids and z‑dna. Circular dna that is not supercoiled (see supercoil), and instead has an unwound.
Solved A closedcircular DNA molecule of 5000 bp has a
But when twisted — as it normally does when squeezing into a cell — the dna morphed into many other. The relaxed circular form of plasmids is often inactive or poorly active. Web the dna full form is deoxyribonucleic acid. Web if such a relaxed dna circle with a nick was ligated, it would have the highest chance to form.
"DNA helix conformation Print Aform Bform Cform and Zform DNA
The relaxed structure on the left is not found unless the chromosome is nicked; Web if such a relaxed dna circle with a nick was ligated, it would have the highest chance to form a dna topoisomer having an lk = 76. Circular dna that is not supercoiled (see supercoil), and instead has an unwound loop. Web a‑form nucleic acids.
Natural molecule derivatives as Topoisomerase Poisons Insights into
Circular dna that is not supercoiled (see supercoil), and instead has an unwound loop. Relaxed, uncoiled, unorganized form of dna,. Web the full form of dna is deoxyribonucleic acid. Web higher molecular weight forms of the plasmid can also sometimes be seen, including a nicked or relaxed form, referred to as open circular, which typically migrates. A phase of mitosis.
(a) The mechanism of type I DNA topoisomerase. The enzymes nick a
Web higher molecular weight forms of the plasmid can also sometimes be seen, including a nicked or relaxed form, referred to as open circular, which typically migrates. What happens when dna is relaxed?. The relaxed circular form of plasmids is often inactive or poorly active. The lk of a dna topoisomer that. A phase of mitosis in which chromosomes become.
(A) Diagram of the supercoiled DNA plasmid electrophoresis gel
Web the explanation was that torsional effects on plasmid dna are mediated by membrane anchoring in the absence of full relaxing power of top i. Web what is relaxed dna? Relaxed, uncoiled, unorganized form of dna,. The supercoiled form is energetically favoured over the. Circular dna that is not supercoiled (see supercoil), and instead has an unwound loop.
Plasmid DNA exists in different forms. Download Scientific Diagram
But when twisted — as it normally does when squeezing into a cell — the dna morphed into many other. Web the dna full form is deoxyribonucleic acid. The lk of a dna topoisomer that. The supercoiled form is energetically favoured over the. A phase of mitosis in which chromosomes become visible and nuclear membrane disappears.
DNA supercoiling. A. A linear doublestranded DNA a
A phase of mitosis in which chromosomes become visible and nuclear membrane disappears. Cell cycle is made of 3 parts: Dna is a set of molecules responsible for the transmitting and carrying the inherited materials or genetic instructions from parents to. Web catch the top stories of the day on anc’s ‘top story’ (28 july 2023) Web higher molecular weight.
The Supercoiled Form Is Energetically Favoured Over The.
Circular dna that is not supercoiled (see supercoil), and instead has an unwound loop. The relaxed structure on the left is not found unless the chromosome is nicked; Web if such a relaxed dna circle with a nick was ligated, it would have the highest chance to form a dna topoisomer having an lk = 76. The relaxed circular form of plasmids is often inactive or poorly active.
Web The Explanation Was That Torsional Effects On Plasmid Dna Are Mediated By Membrane Anchoring In The Absence Of Full Relaxing Power Of Top I.
But when twisted — as it normally does when squeezing into a cell — the dna morphed into many other. Web higher molecular weight forms of the plasmid can also sometimes be seen, including a nicked or relaxed form, referred to as open circular, which typically migrates. Relaxed, uncoiled, unorganized form of dna,. Circular dna that is not supercoiled (see supercoil), and instead has an unwound loop.
Web The Relaxed Form Of Dna In The Cell's Nucleus.
The most common form, present in most dna at neutral ph and. Web supercoiled state corresponds to the active form for plasmid applications. Web what is relaxed dna? Cell cycle is made of 3 parts:
Web The Dna Full Form Is Deoxyribonucleic Acid.
Dna is a set of molecules responsible for the transmitting and carrying the inherited materials or genetic instructions from parents to. A phase of mitosis in which chromosomes become visible and nuclear membrane disappears. Web a‑form nucleic acids and z‑dna. Circular dna that is not supercoiled (see supercoil), and instead has an unwound loop.