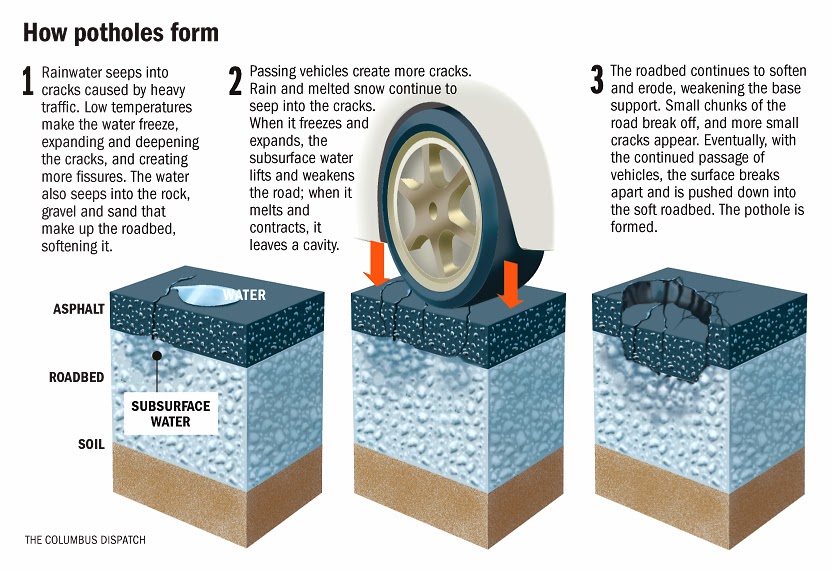
How Does A Pothole Form
How Does A Pothole Form - Web it drives the asphalt into the gaps created by the melted ice. Potholes form naturally due to many elemental forces in action. Water first weakens the underlying soil; It is usually the result of water in the underlying soil structure and traffic passing over the affected area. Web most potholes are caused by water which seeps into existing small cracks in the surface of the road caused by the wear and tear of traffic and deterioration over time. Web a pothole is a depression in a road surface, usually asphalt pavement, where traffic has removed broken pieces of the pavement. When water freezes, it expands. Web potholes are holes in the roadway that vary in size and shape. What part does weather paly in creating potholes? During cold weather, freezing temperatures cause the liquid water to freeze and expand.
What part does weather paly in creating potholes? First, water from rain or melted snow seeps into pavement through small cracks and rests underneath the upper pavement. Web how does a pothole form? Web how do potholes form? They are caused by the expansion and contraction of ground water after the water has entered into the ground under the pavement. Over a period of time, the entire process results in a hole that’s destined to make you spill your coffee. Web what causes potholes? Potholes are created when water makes its way into cracks in the pavement and softens the ground underneath, allowing the road to cave in or crack further under pressure. A naturally formed pothole in south africa. It is usually the result of water in the underlying soil structure and traffic passing over the affected area.
Web a pothole is a depression in a road surface, usually asphalt pavement, where traffic has removed broken pieces of the pavement. Web how do potholes form? Water first weakens the underlying soil; Web how does a pothole form? Web most potholes are caused by water which seeps into existing small cracks in the surface of the road caused by the wear and tear of traffic and deterioration over time. Typically, potholes develop when moisture permeates a paved surface or when the groundwater beneath the pavement penetrates the paved surface. A naturally formed pothole in south africa. Cold weather then causes this water to freeze (and expand) and when this water melts and evaporates in the warmer weather, it creates gaps which then get broken down by the. During cold weather, freezing temperatures cause the liquid water to freeze and expand. Web potholes are holes in the roadway that vary in size and shape.
GC6V1V9 Harburn Wells (Multicache) in Ontario, Canada created by B.A.M
They are caused by the expansion and contraction of ground water after the water has entered into the ground under the pavement. During cold weather, freezing temperatures cause the liquid water to freeze and expand. Other names used for riverine potholes are pot, (stream) kettle, giant's kettle, evorsion, hollow,. It is usually the result of water in the underlying soil.
How Potholes Form YouTube
Traffic then fatigues and breaks the poorly supported asphalt. Web it drives the asphalt into the gaps created by the melted ice. Web as far as the actual process goes, potholes are basically formed by water and gravity: Over a period of time, the entire process results in a hole that’s destined to make you spill your coffee. Potholes form.
Why Is It Called a Pothole? How Do They Form?
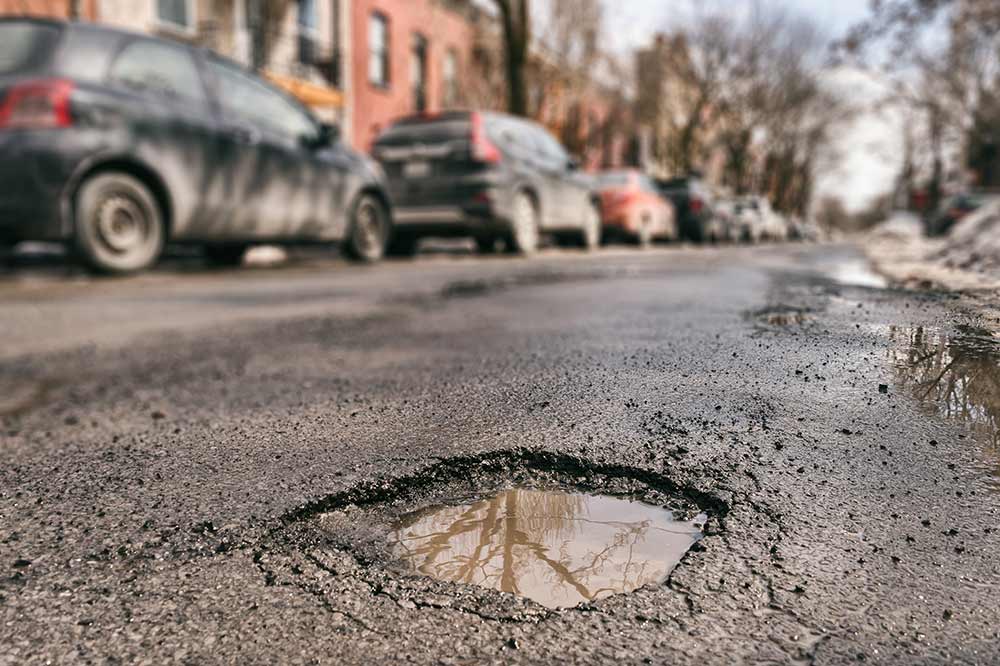
A naturally formed pothole in south africa. Web most potholes are caused by water which seeps into existing small cracks in the surface of the road caused by the wear and tear of traffic and deterioration over time. First, water from rain or melted snow seeps into pavement through small cracks and rests underneath the upper pavement. When water freezes,.
How does a pothole form YouTube
Web potholes are holes in the roadway that vary in size and shape. Other names used for riverine potholes are pot, (stream) kettle, giant's kettle, evorsion, hollow,. Web it drives the asphalt into the gaps created by the melted ice. Web most potholes are caused by water which seeps into existing small cracks in the surface of the road caused.
Potholes Everyone's Favorite in Spring
Over a period of time, the entire process results in a hole that’s destined to make you spill your coffee. During cold weather, freezing temperatures cause the liquid water to freeze and expand. They are caused by the expansion and contraction of ground water after the water has entered into the ground under the pavement. Web how do potholes form?.
How Do Potholes Form? (And Why You Should Repair Them ASAP)
When water freezes, it expands. Web what causes potholes? Potholes form naturally due to many elemental forces in action. First, water from rain or melted snow seeps into pavement through small cracks and rests underneath the upper pavement. Traffic then fatigues and breaks the poorly supported asphalt.
How do potholes form?
Typically, potholes develop when moisture permeates a paved surface or when the groundwater beneath the pavement penetrates the paved surface. During cold weather, freezing temperatures cause the liquid water to freeze and expand. Web how do potholes form? First, water from rain or melted snow seeps into pavement through small cracks and rests underneath the upper pavement. It is usually.
Potholes Meaning, causes, and fixes
Other names used for riverine potholes are pot, (stream) kettle, giant's kettle, evorsion, hollow,. Web what causes potholes? Over a period of time, the entire process results in a hole that’s destined to make you spill your coffee. Web most potholes are caused by water which seeps into existing small cracks in the surface of the road caused by the.
The Munson, Inc. Blog Potholes and Frost Heave in Milwaukee
Water first weakens the underlying soil; During cold weather, freezing temperatures cause the liquid water to freeze and expand. Web potholes are holes in the roadway that vary in size and shape. Web how does a pothole form? A naturally formed pothole in south africa.
How does a pothole form?
Web how do potholes form? Traffic then fatigues and breaks the poorly supported asphalt. They are caused by the expansion and contraction of ground water after the water has entered into the ground under the pavement. Water first weakens the underlying soil; Web potholes are holes in the roadway that vary in size and shape.
What Part Does Weather Paly In Creating Potholes?
Typically, potholes develop when moisture permeates a paved surface or when the groundwater beneath the pavement penetrates the paved surface. Water first weakens the underlying soil; Other names used for riverine potholes are pot, (stream) kettle, giant's kettle, evorsion, hollow,. They are caused by the expansion and contraction of ground water after the water has entered into the ground under the pavement.
Web Potholes Are Holes In The Roadway That Vary In Size And Shape.
First, water from rain or melted snow seeps into pavement through small cracks and rests underneath the upper pavement. ( source) so, it was an easy segue into calling these holes that form on our roads, which have a similar shape, the same thing. A naturally formed pothole in south africa. Cold weather then causes this water to freeze (and expand) and when this water melts and evaporates in the warmer weather, it creates gaps which then get broken down by the.
Web How Does A Pothole Form?
Web it drives the asphalt into the gaps created by the melted ice. Web how do potholes form? Web a pothole is a depression in a road surface, usually asphalt pavement, where traffic has removed broken pieces of the pavement. Over a period of time, the entire process results in a hole that’s destined to make you spill your coffee.
When Water Freezes, It Expands.
Potholes form naturally due to many elemental forces in action. Web as far as the actual process goes, potholes are basically formed by water and gravity: Potholes are created when water makes its way into cracks in the pavement and softens the ground underneath, allowing the road to cave in or crack further under pressure. It is usually the result of water in the underlying soil structure and traffic passing over the affected area.