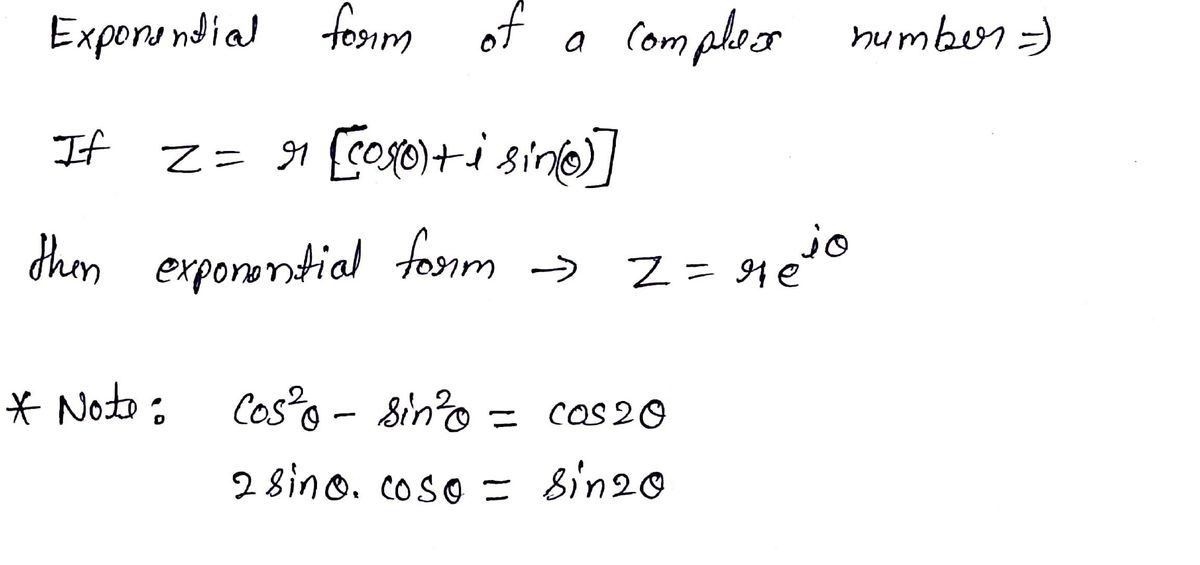Cos To Exponential Form
Cos To Exponential Form - Reiθ = r(cos(θ) + isin(θ)) products of complex numbers in polar form there is an important. Web $$e^{ix} = \cos x + i \sin x$$ fwiw, that formula is valid for complex $x$ as well as real $x$. Web unlock pro cos^2 (x) natural language math input extended keyboard examples random I tried to find something about it by googling but only get complex exponential to sine/cosine conversion. Web hyperbolic functions in mathematics, hyperbolic functions are analogues of the ordinary trigonometric functions, but defined using the hyperbola rather than the circle. Web eiθ = cos(θ) + isin(θ) so the polar form r(cos(θ) + isin(θ)) can also be written as reiθ: Ψ(x, t) = a cos(kx − ωt + ϕ) ψ ( x, t) = a cos ( k x − ω t + ϕ) attempt: (45) (46) (47) from these relations and the properties of exponential multiplication you can painlessly prove all. Web using the exponential forms of cos(theta) and sin(theta) given in (3.11a, b), prove the following trigonometric identities: A) sin(x + y) = sin(x)cos(y) + cos(x)sin(y) and.
Web i want to write the following in exponential form: I tried to find something about it by googling but only get complex exponential to sine/cosine conversion. Web complex exponential form a plane sinusoidal wave may also be expressed in terms of the complex exponential function e i z = exp ( i z ) = cos z + i sin z {\displaystyle. Web according to euler, we should regard the complex exponential eit as related to the trigonometric functions cos(t) and sin(t) via the following inspired definition: A) sin(x + y) = sin(x)cos(y) + cos(x)sin(y) and. Ψ(x, t) = r{aei(kx−ωt+ϕ)} = r{aeiϕei(kx−ωt)} =. Web hyperbolic functions in mathematics, hyperbolic functions are analogues of the ordinary trigonometric functions, but defined using the hyperbola rather than the circle. $\exp z$ denotes the exponential function $\cos z$ denotes the complex cosine function $i$. Web eiθ = cos(θ) + isin(θ) so the polar form r(cos(θ) + isin(θ)) can also be written as reiθ: Web an exponential equation is an equation that contains an exponential expression of the form b^x, where b is a constant (called the base) and x is a variable.
Web hyperbolic functions in mathematics, hyperbolic functions are analogues of the ordinary trigonometric functions, but defined using the hyperbola rather than the circle. Web in fact, the functions sin and cos can be defined for all complex numbers in terms of the exponential function, via power series, [6] or as solutions to differential equations given. $\exp z$ denotes the exponential function $\cos z$ denotes the complex cosine function $i$. Web an exponential equation is an equation that contains an exponential expression of the form b^x, where b is a constant (called the base) and x is a variable. Web using the exponential forms of cos(theta) and sin(theta) given in (3.11a, b), prove the following trigonometric identities: Eit = cos t + i. Ψ(x, t) = r{aei(kx−ωt+ϕ)} = r{aeiϕei(kx−ωt)} =. Web according to euler, we should regard the complex exponential eit as related to the trigonometric functions cos(t) and sin(t) via the following inspired definition: Web the exponential function is defined on the entire domain of the complex numbers. Reiθ = r(cos(θ) + isin(θ)) products of complex numbers in polar form there is an important.
EM to Optics 10 Converting Cos & Sine to Complex Exponentials YouTube
Reiθ = r(cos(θ) + isin(θ)) products of complex numbers in polar form there is an important. $\exp z$ denotes the exponential function $\cos z$ denotes the complex cosine function $i$. I tried to find something about it by googling but only get complex exponential to sine/cosine conversion. Web i want to write the following in exponential form: Web eiθ =.
Question Video Converting the Product of Complex Numbers in Polar Form
Web in fact, the functions sin and cos can be defined for all complex numbers in terms of the exponential function, via power series, [6] or as solutions to differential equations given. Web using the exponential forms of cos(theta) and sin(theta) given in (3.11a, b), prove the following trigonometric identities: $\exp z$ denotes the exponential function $\cos z$ denotes the.
FileSine Cosine Exponential qtl1.svg Wikipedia
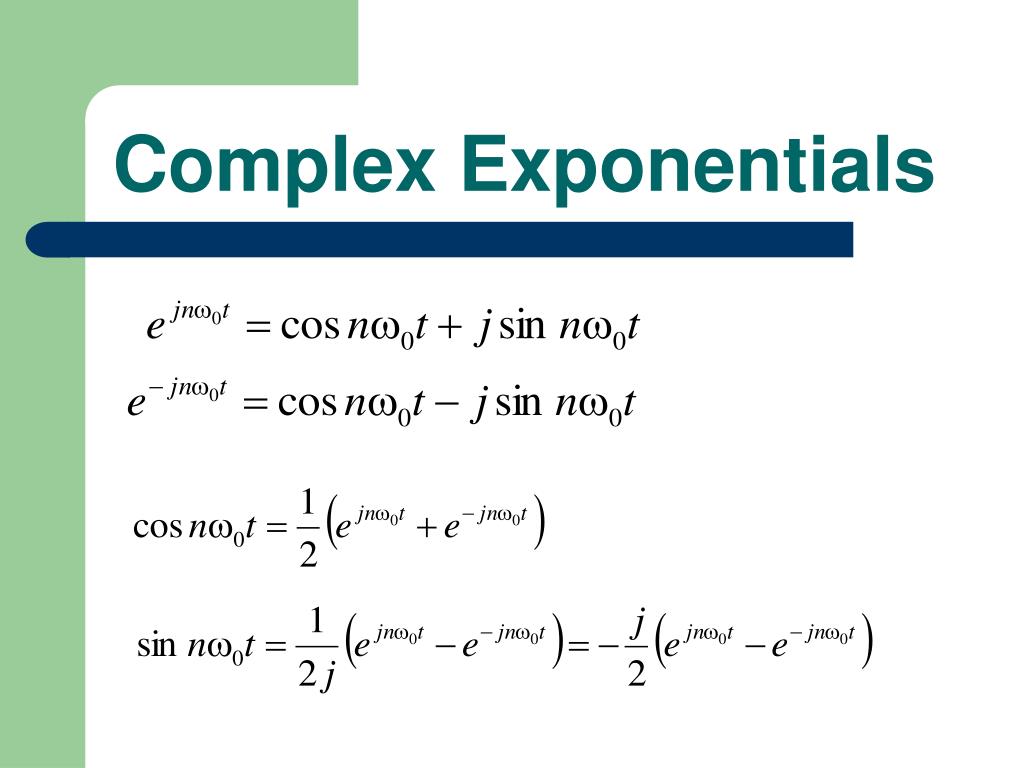
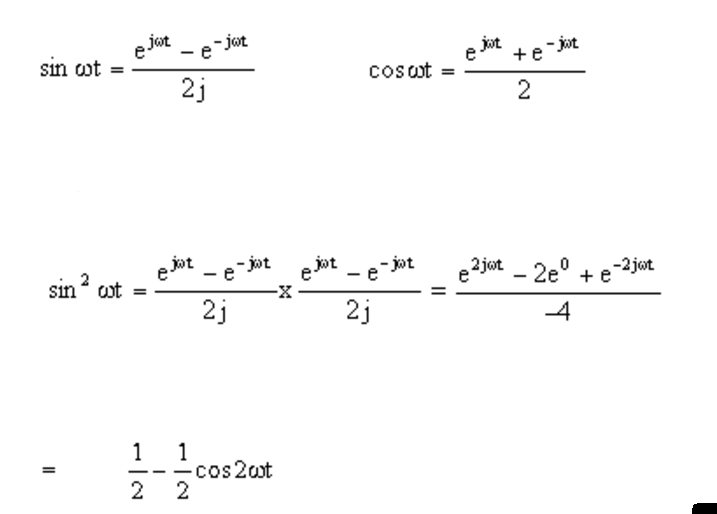
A) sin(x + y) = sin(x)cos(y) + cos(x)sin(y) and. E jx = cos (x) + jsin (x) and the exponential representations of sin & cos, which are derived from euler's formula: Web complex exponential form a plane sinusoidal wave may also be expressed in terms of the complex exponential function e i z = exp ( i z ).
Answered Express (cos(20)+i sin(20))*in… bartleby
Web an exponential equation is an equation that contains an exponential expression of the form b^x, where b is a constant (called the base) and x is a variable. Ψ(x, t) = a cos(kx − ωt + ϕ) ψ ( x, t) = a cos ( k x − ω t + ϕ) attempt: Eit = cos t + i..
PPT Fourier Series PowerPoint Presentation ID390675
Web unlock pro cos^2 (x) natural language math input extended keyboard examples random Web $$e^{ix} = \cos x + i \sin x$$ fwiw, that formula is valid for complex $x$ as well as real $x$. Reiθ = r(cos(θ) + isin(θ)) products of complex numbers in polar form there is an important. Ψ(x, t) = r{aei(kx−ωt+ϕ)} = r{aeiϕei(kx−ωt)} =. E jx.
Basics of QPSK modulation and display of QPSK signals Electrical
Web relations between cosine, sine and exponential functions. Web the exponential function is defined on the entire domain of the complex numbers. Web according to euler, we should regard the complex exponential eit as related to the trigonometric functions cos(t) and sin(t) via the following inspired definition: Ψ(x, t) = a cos(kx − ωt + ϕ) ψ ( x, t).
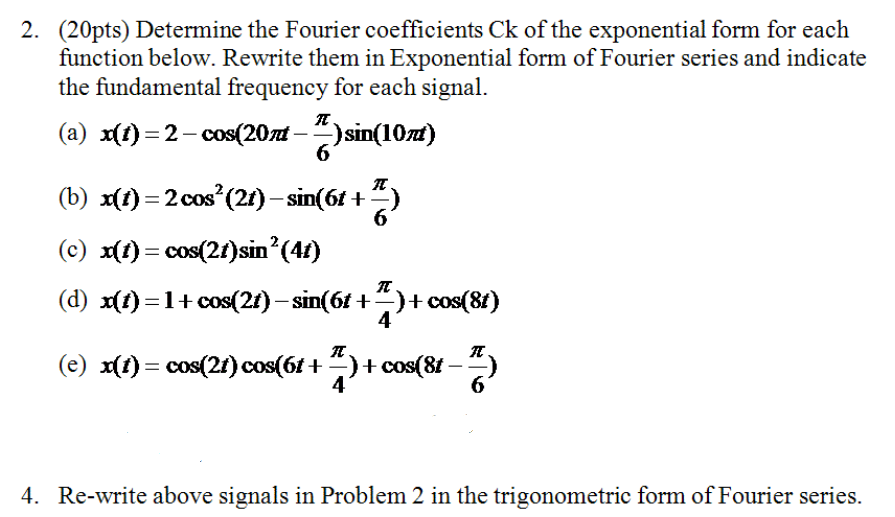
Solved 2. (20pts) Determine the Fourier coefficients Ck of
Reiθ = r(cos(θ) + isin(θ)) products of complex numbers in polar form there is an important. Web i want to write the following in exponential form: Web according to euler, we should regard the complex exponential eit as related to the trigonometric functions cos(t) and sin(t) via the following inspired definition: Web $$e^{ix} = \cos x + i \sin x$$.
Complex Numbers 4/4 Cos and Sine to Complex Exponential YouTube
I tried to find something about it by googling but only get complex exponential to sine/cosine conversion. A) sin(x + y) = sin(x)cos(y) + cos(x)sin(y) and. Eit = cos t + i. Web an exponential equation is an equation that contains an exponential expression of the form b^x, where b is a constant (called the base) and x is a.
Question Video Dividing Complex Numbers in Polar Form and Expressing
A) sin(x + y) = sin(x)cos(y) + cos(x)sin(y) and. Web $$e^{ix} = \cos x + i \sin x$$ fwiw, that formula is valid for complex $x$ as well as real $x$. Ψ(x, t) = a cos(kx − ωt + ϕ) ψ ( x, t) = a cos ( k x − ω t + ϕ) attempt: Web in fact, the.
[Solved] I need help with this question Determine the Complex
Web unlock pro cos^2 (x) natural language math input extended keyboard examples random Web the exponential function is defined on the entire domain of the complex numbers. Web in fact, the functions sin and cos can be defined for all complex numbers in terms of the exponential function, via power series, [6] or as solutions to differential equations given. Ψ(x,.
A) Sin(X + Y) = Sin(X)Cos(Y) + Cos(X)Sin(Y) And.
Web unlock pro cos^2 (x) natural language math input extended keyboard examples random Web eiθ = cos(θ) + isin(θ) so the polar form r(cos(θ) + isin(θ)) can also be written as reiθ: Web complex exponential form a plane sinusoidal wave may also be expressed in terms of the complex exponential function e i z = exp ( i z ) = cos z + i sin z {\displaystyle. $\exp z$ denotes the exponential function $\cos z$ denotes the complex cosine function $i$.
Ψ(X, T) = A Cos(Kx − Ωt + Φ) Ψ ( X, T) = A Cos ( K X − Ω T + Φ) Attempt:
Web relations between cosine, sine and exponential functions. Ψ(x, t) = r{aei(kx−ωt+ϕ)} = r{aeiϕei(kx−ωt)} =. The definition of sine and cosine can be extended to all complex numbers via these can be. Eit = cos t + i.
Web $$E^{Ix} = \Cos X + I \Sin X$$ Fwiw, That Formula Is Valid For Complex $X$ As Well As Real $X$.
I tried to find something about it by googling but only get complex exponential to sine/cosine conversion. Web according to euler, we should regard the complex exponential eit as related to the trigonometric functions cos(t) and sin(t) via the following inspired definition: Web the exponential function is defined on the entire domain of the complex numbers. Web in fact, the functions sin and cos can be defined for all complex numbers in terms of the exponential function, via power series, [6] or as solutions to differential equations given.
Web I Want To Write The Following In Exponential Form:
E jx = cos (x) + jsin (x) and the exponential representations of sin & cos, which are derived from euler's formula: Web an exponential equation is an equation that contains an exponential expression of the form b^x, where b is a constant (called the base) and x is a variable. (45) (46) (47) from these relations and the properties of exponential multiplication you can painlessly prove all. Web hyperbolic functions in mathematics, hyperbolic functions are analogues of the ordinary trigonometric functions, but defined using the hyperbola rather than the circle.