Chapter 5 The Structure And Function Of Macromolecules
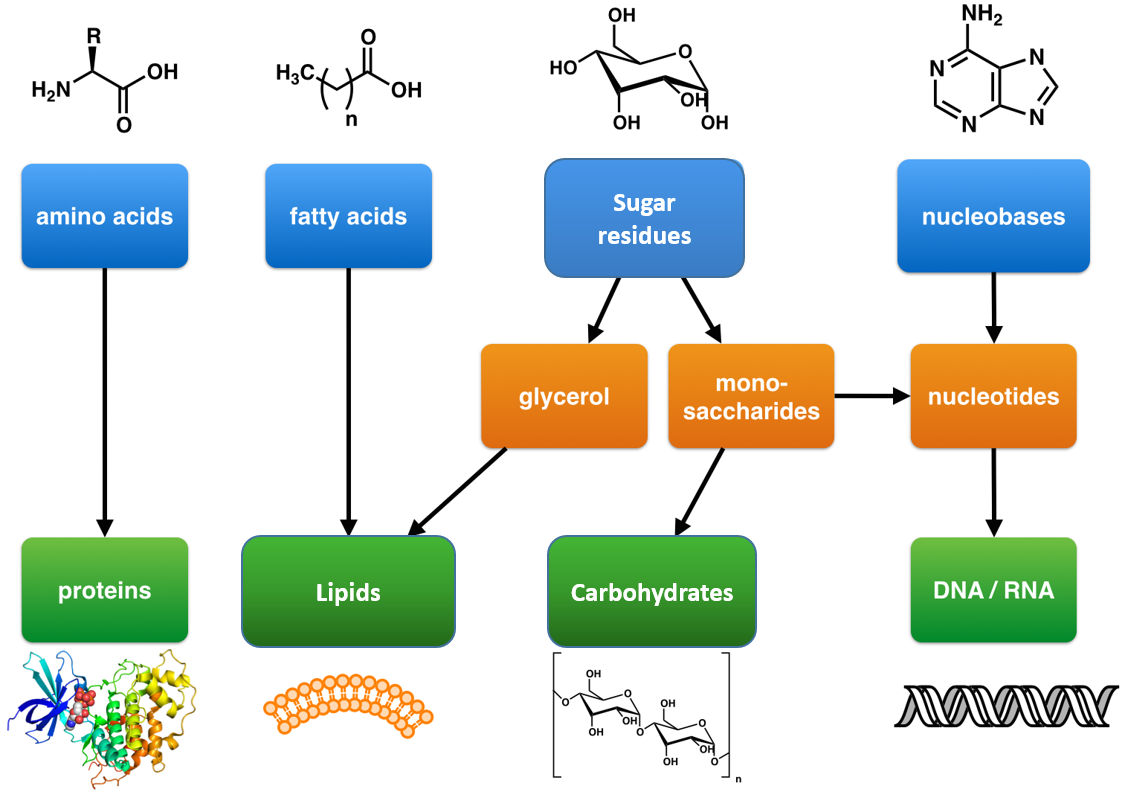
Chapter 5 The Structure And Function Of Macromolecules - Web a giant molecule formed by the joining of smaller molecules, usually by a dehydration reaction. The structure and function of macromolecules 4.2 (14 reviews) macromolecule click the card to. The structure and function of macromol ecules: Within cells, small organic molecules are joined together to. Are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.the molecules of life. The molecules of life • within all cells,. Breaking of a polymer with an addition of water. Web the structure and function of carbohydrates (25 marks) carbohydrates are made from carbon (c), hydrogen (h) and oxygen (o). Web chapter 5 the structure and function of macromolecules. Web terms in this set (59) molecular structure and function are inseperable.
Concept 5.1 macromolecules are polymers, built from. The molecules of life within cells, small. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with. The structure and function of large biological molecules. Web terms in this set (59) molecular structure and function are inseperable. Web created by nataliehauser58 terms in this set (60) macromolecules a very large organic molecule composed of many smaller. Web the structure and function of carbohydrates (25 marks) carbohydrates are made from carbon (c), hydrogen (h) and oxygen (o). Within cells, small organic molecules are joined together to. Web please click the link below to download the biology slides from the campbell’s biology, 7th edition textbook. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic.
The molecules of life within cells, small. The structure and function of macromolecules 4.2 (14 reviews) macromolecule click the card to. The structure and function of large biological molecules. Web · three levels of structure—primary, secondary, and tertiary structures—organize the folding within a single polypeptide. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with. Web ap biology ch 5: Web please click the link below to download the biology slides from the campbell’s biology, 7th edition textbook. Web created by nataliehauser58 terms in this set (60) macromolecules a very large organic molecule composed of many smaller. Are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.the molecules of life. Web terms in this set (59) molecular structure and function are inseperable.
Apch5ppt
Web please click the link below to download the biology slides from the campbell’s biology, 7th edition textbook. Web chapter 5 the structure and function of macromolecules. Web there are four classes of macromolecules that constitute all living matter: Breaking of a polymer with an addition of water. Concept 5.1 macromolecules are polymers, built from.
Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of
Web terms in this set (59) molecular structure and function are inseperable. Are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.the molecules of life. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with. The structure and function of macromolecules 4.2 (14 reviews) macromolecule click the card to. Web chapter 5 the structure and function of macromolecules.
PPT CHAPTER 3 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules PowerPoint
Web the structure and function of carbohydrates (25 marks) carbohydrates are made from carbon (c), hydrogen (h) and oxygen (o). Web chapter 5 the structure and function of macromolecules lecture outline. Are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.the molecules of life. The molecules of life • within all cells,. What are the major types of organic mo lecules?
Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic. Web terms in this set (59) molecular structure and function are inseperable. Web there are four classes of macromolecules that constitute all living matter: Are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.the molecules of life. Within cells, small organic molecules are joined together to.
GR 9 Topic 3 Macro Molecules AMAZING WORLD OF SCIENCE WITH MR. GREEN
Web terms in this set (59) molecular structure and function are inseperable. Web created by nataliehauser58 terms in this set (60) macromolecules a very large organic molecule composed of many smaller. Web the structure and function of carbohydrates (25 marks) carbohydrates are made from carbon (c), hydrogen (h) and oxygen (o). The molecules of life within cells, small. Web ap.
PPT Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules PowerPoint
What are the major types of organic mo lecules? Web please click the link below to download the biology slides from the campbell’s biology, 7th edition textbook. Web chapter 5 the structure and function of macromolecules lecture outline. Within cells, small organic molecules are joined together to. Web a giant molecule formed by the joining of smaller molecules, usually by.
Chapter 5 Macromolecules
Web · three levels of structure—primary, secondary, and tertiary structures—organize the folding within a single polypeptide. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic. Web the four major classes of macromolecules. The structure and function of macromolecules 4.2 (14 reviews) macromolecule click the card to. The molecules of life within cells, small.
PPT CHAPTER 5 THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF MACROMOLECULES PowerPoint
What are the major types of organic mo lecules? The structure and function of large biological macromolecules. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic. Are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.the molecules of life. The molecules of life within cells, small.
PPT CHAPTER 5 THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF MACROMOLECULES PowerPoint
The structure and function of large biological macromolecules. The molecules of life within cells, small. Web a giant molecule formed by the joining of smaller molecules, usually by a dehydration reaction. Within cells, small organic molecules are joined together to. Web chapter 5 the structure and function of macromolecules lecture outline.
Macromolecules Lecture
Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with. The structure and function of macromolecules 4.2 (14 reviews) macromolecule click the card to. Web a giant molecule formed by the joining of smaller molecules, usually by a dehydration reaction. Breaking of a polymer with an addition of water. Web please click the link below to download the biology slides from the campbell’s biology,.
Web Terms In This Set (59) Molecular Structure And Function Are Inseperable.
Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with. What are the major types of organic mo lecules? The structure and function of macromolecules 4.2 (14 reviews) macromolecule click the card to. Concept 5.1 macromolecules are polymers, built from.
The Molecules Of Life Within Cells, Small.
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic. Are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.the molecules of life. The structure and function of macromol ecules: Web please click the link below to download the biology slides from the campbell’s biology, 7th edition textbook.
Web Ap Biology Ch 5:
The molecules of life • within all cells,. Web the four major classes of macromolecules. The structure and function of large biological macromolecules. Web chapter 5 the structure and function of macromolecules lecture outline.
Web Chapter 5 The Structure And Function Of Macromolecules.
The structure and function of large biological molecules. Web a giant molecule formed by the joining of smaller molecules, usually by a dehydration reaction. Web · three levels of structure—primary, secondary, and tertiary structures—organize the folding within a single polypeptide. Breaking of a polymer with an addition of water.