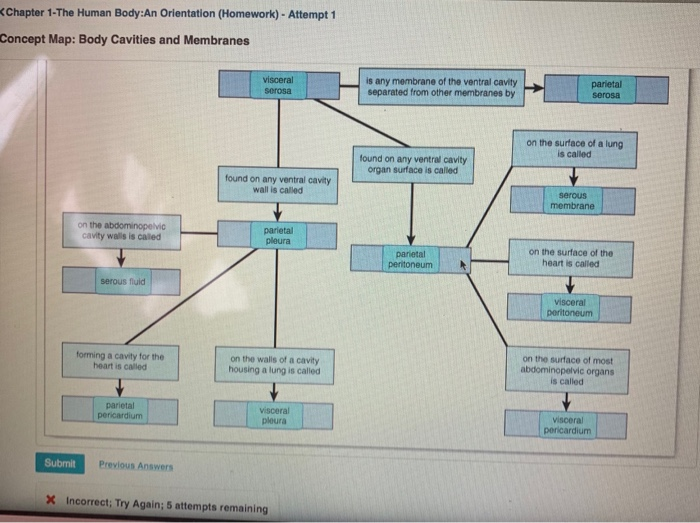
Chapter 1 The Human Body An Orientation Quizlet
Chapter 1 The Human Body An Orientation Quizlet - Web higher levels of organization are built from lower levels. Web the human body is shown in anatomical position in an (a) anterior view and a (b) posterior view. The human body is shown in anatomical position in an (a) anterior view and a (b). Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like anatomy, physiology, gross anatomy and more. Web study flashcards on chapter 1 the human body an orientation at cram.com. Levels of structural organization (6) atomic, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system,. An introduction to the human body ; Web describe the structure of the body, from simplest to most complex, in terms of the six levels of organization; A type of gross anatomy where it examines internal structures relating to overlaying skin. Web © 2023 quizlet, inc.
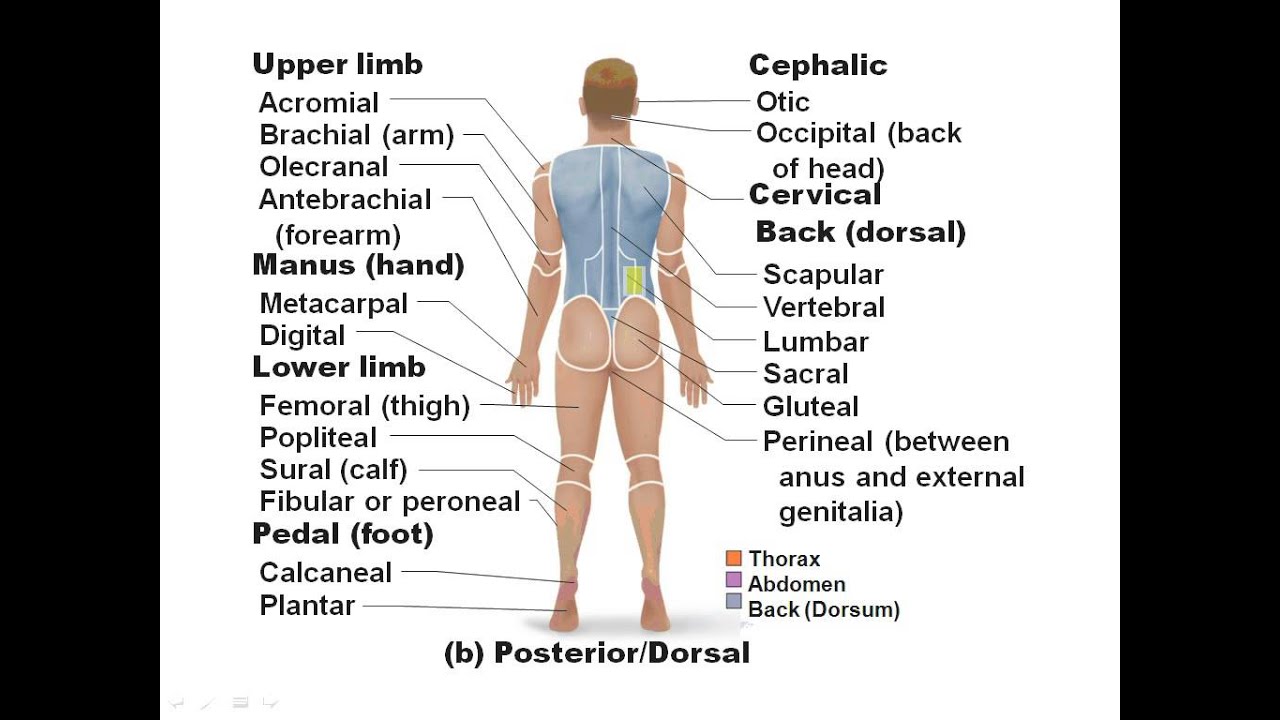
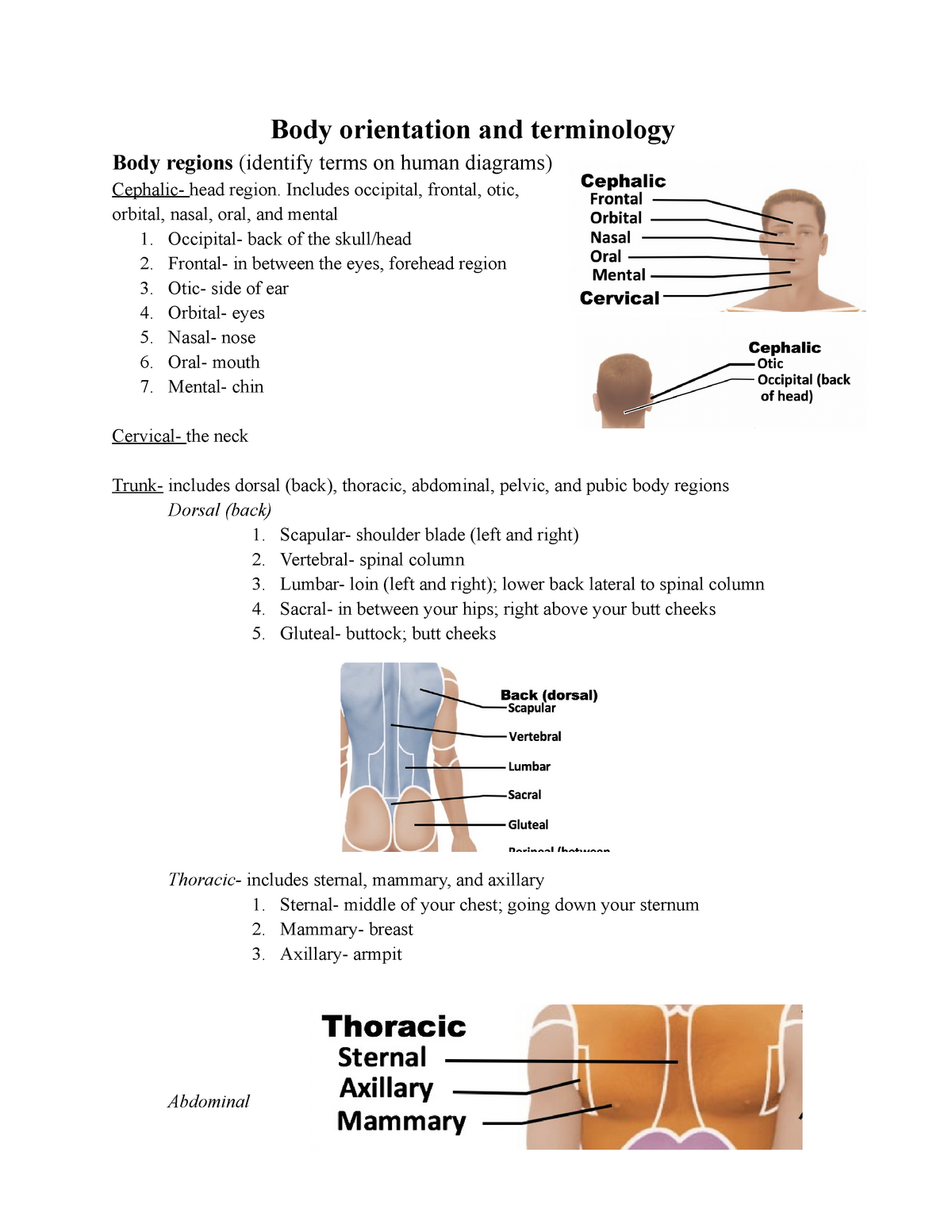
What a structure can do depends on the specific. The regions of the body are. The tissue level of organization ; Web study flashcards on chapter 1 the human body an orientation at cram.com. Web © 2023 quizlet, inc. Web figure 1.12 regions of the human body the human body is shown in anatomical position in an (a) anterior view and a (b) posterior. Web the human body is shown in anatomical position in an (a) anterior view and a (b) posterior view. Therefore, molecules combine to form cells, cells combine to form. Web higher levels of organization are built from lower levels. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other.
Inferior (caudal) away from the head end or toward the lower part of a structure or the. Web anatomy and physiology chapter 1 the human body an orientation packet answers 1 anatomy and physiology chapter 1 the. Web start studying chapter 1: Therefore, molecules combine to form cells, cells combine to form. Web to be able to direct others to specific anatomical structures, or to find structures based on someone else’s directions, it is. What a structure can do depends on the specific. Identify three planes most commonly used in the study of. The tissue level of organization ; Web the head is ___________ to the abdomen. Web study flashcards on chapter 1 the human body an orientation at cram.com.
Anatomy And Physiology Chapter 1 Quizlet
An introduction to the human body ; Web one of the descriptions below is from the perspective of anatomical study, the rest are from a physiological perspective. Web higher levels of organization are built from lower levels. Web © 2023 quizlet, inc. Levels of structural organization (6) atomic, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system,.
Anatomy Body Orientation Other Quiz Quizizz
Web study flashcards on chapter 1 the human body an orientation at cram.com. Inferior (caudal) away from the head end or toward the lower part of a structure or the. Closer to the orgin of the body part (or pt of attach) 3. Web start studying chapter 1: An introduction to the human body ;
A&P I chapter 1 orientation YouTube
What a structure can do depends on the specific. The regions of the body are. Web figure 1.12 regions of the human body the human body is shown in anatomical position in an (a) anterior view and a (b) posterior. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other. Web start studying chapter 1:
Chapter 1 The Human Body An Orientation
Levels of structural organization (6) atomic, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system,. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other. Web the study of large body structures, visible to the naked eye, such as the heart, lungs, or kidney is called ____ anatomy? Quickly memorize the terms, phrases and much. Web describe the human body using directional and regional.
Chapter 1 The Human Body An Orientation Worksheet Answers
Therefore, molecules combine to form cells, cells combine to form. Between a more medial and more lateral structure. Web figure 1.12 regions of the human body the human body is shown in anatomical position in an (a) anterior view and a (b) posterior. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like anatomy, physiology, gross anatomy and more. Web.
Chapter 1 The Human Body An Orientation
The tissue level of organization ; Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like anatomy, physiology, gross anatomy and more. The human body is shown in anatomical position in an (a) anterior view and a (b). Web anatomy and physiology chapter 1 the human body an orientation packet answers 1 anatomy and physiology chapter 1 the. Web the.
Copy of Lab 1 Quiz Review sheet for body orientation lab quiz Body
Quickly memorize the terms, phrases and much. Closer to the orgin of the body part (or pt of attach) 3. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like anatomy, physiology, gross anatomy and more. What a structure can do depends on the specific. Web higher levels of organization are built from lower levels.
PPT CHAPTER 1 The Human Body An Orientation PowerPoint Presentation
Web figure 1.12 regions of the human body the human body is shown in anatomical position in an (a) anterior view and a (b) posterior. Web start studying chapter 1: Web the human body is shown in anatomical position in an (a) anterior view and a (b) posterior view. 8 questions | by phynex03 | updated: Therefore, molecules combine to.
Chapter 1 The Human Body An Orientation Answers Islero Guide Answer
Levels of structural organization (6) atomic, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system,. Web the study of large body structures, visible to the naked eye, such as the heart, lungs, or kidney is called ____ anatomy? Web the head is ___________ to the abdomen. The human body is shown in anatomical position in an (a) anterior view and a (b). Web describe.
Chapter 1 The Human Body An Orientation
8 questions | by phynex03 | updated: Web to be able to direct others to specific anatomical structures, or to find structures based on someone else’s directions, it is. Web higher levels of organization are built from lower levels. Web study flashcards on chapter 1 the human body an orientation at cram.com. Web study of the function of the body's.
Web Describe The Human Body Using Directional And Regional Terms;
An introduction to the human body ; Web to be able to direct others to specific anatomical structures, or to find structures based on someone else’s directions, it is. Web the head is ___________ to the abdomen. Web start studying chapter 1:
Inferior (Caudal) Away From The Head End Or Toward The Lower Part Of A Structure Or The.
Therefore, molecules combine to form cells, cells combine to form. The tissue level of organization ; A type of gross anatomy where it examines internal structures relating to overlaying skin. Web describe the structure of the body, from simplest to most complex, in terms of the six levels of organization;
Web Chapter 1 The Human Body An Orientation.
Closer to the orgin of the body part (or pt of attach) 3. Web higher levels of organization are built from lower levels. Between a more medial and more lateral structure. Quickly memorize the terms, phrases and much.
Web Study With Quizlet And Memorize Flashcards Containing Terms Like Anatomy, Physiology, Gross Anatomy And More.
Web one of the descriptions below is from the perspective of anatomical study, the rest are from a physiological perspective. Web © 2023 quizlet, inc. Web study flashcards on chapter 1 the human body an orientation at cram.com. Web the human body is shown in anatomical position in an (a) anterior view and a (b) posterior view.