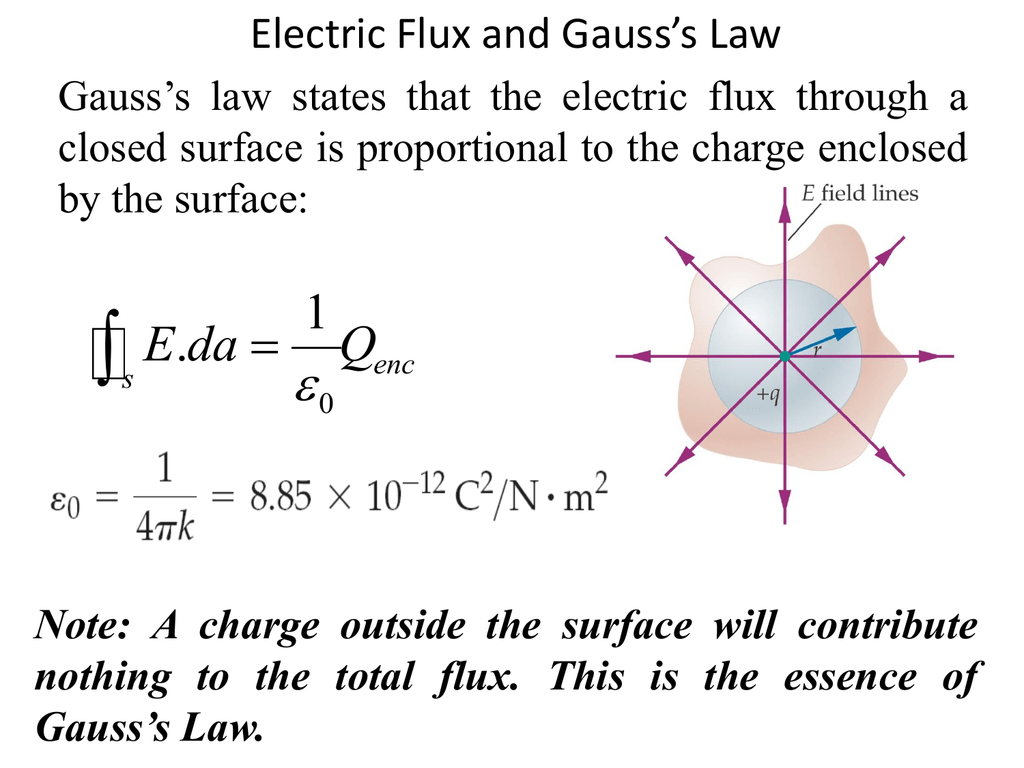
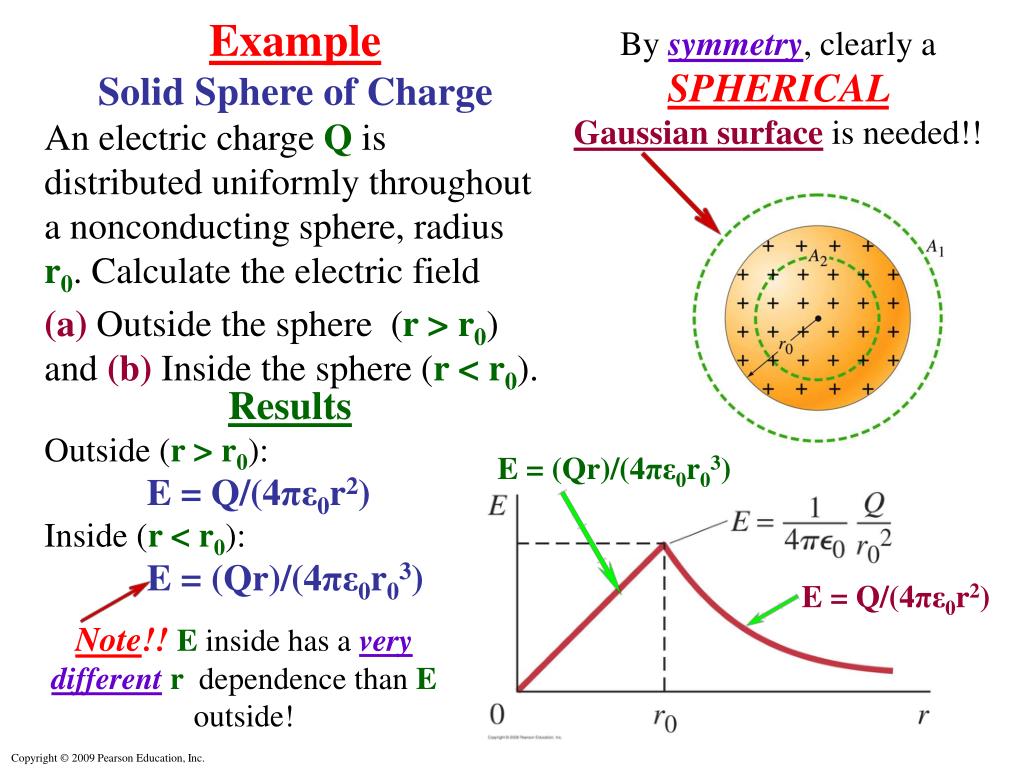
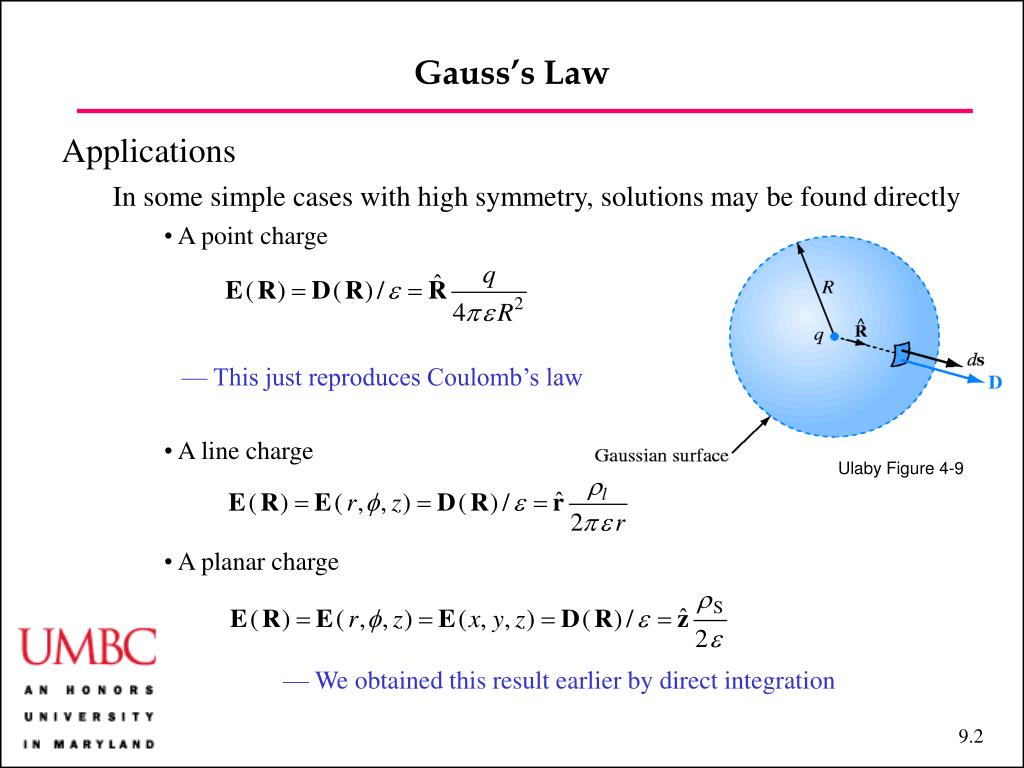
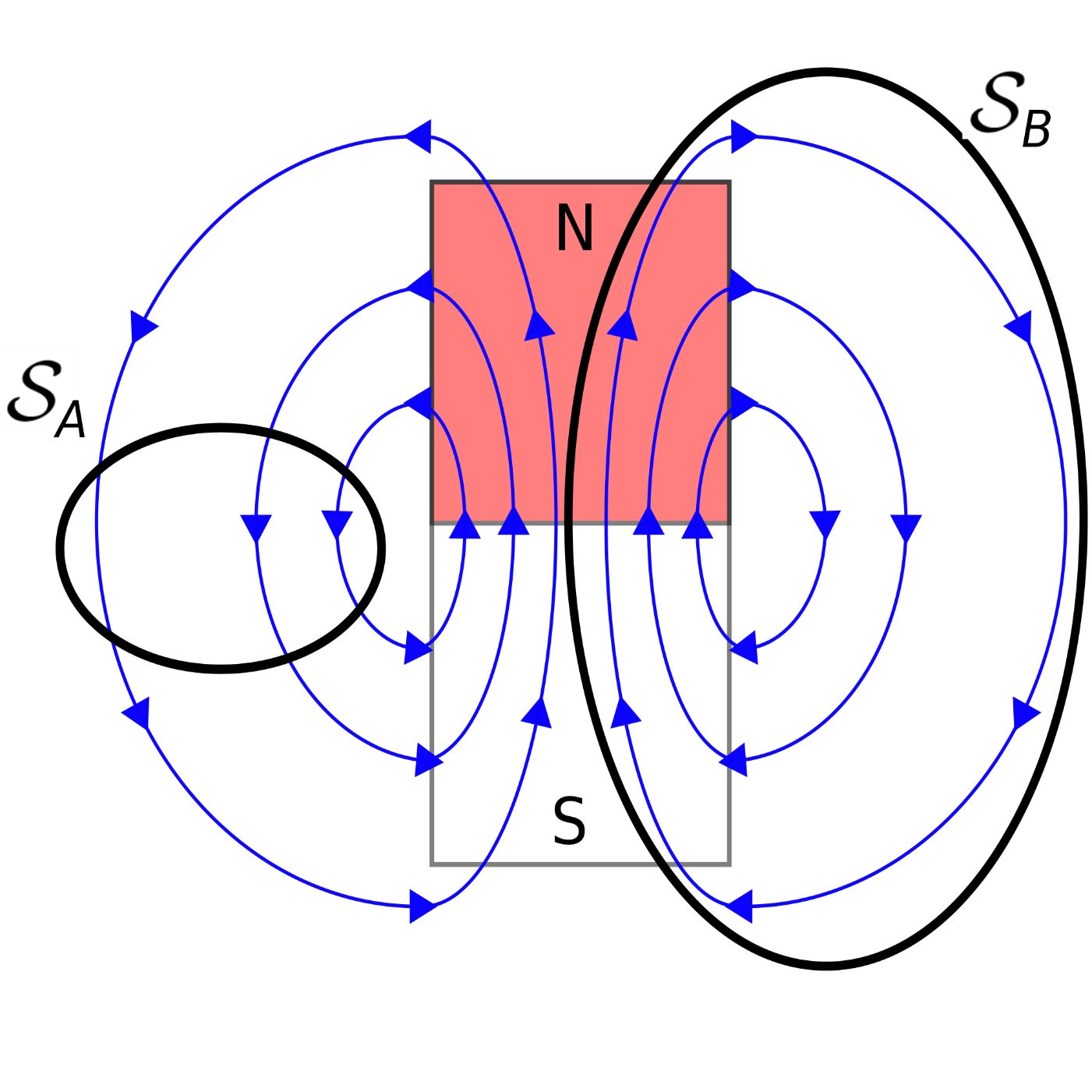
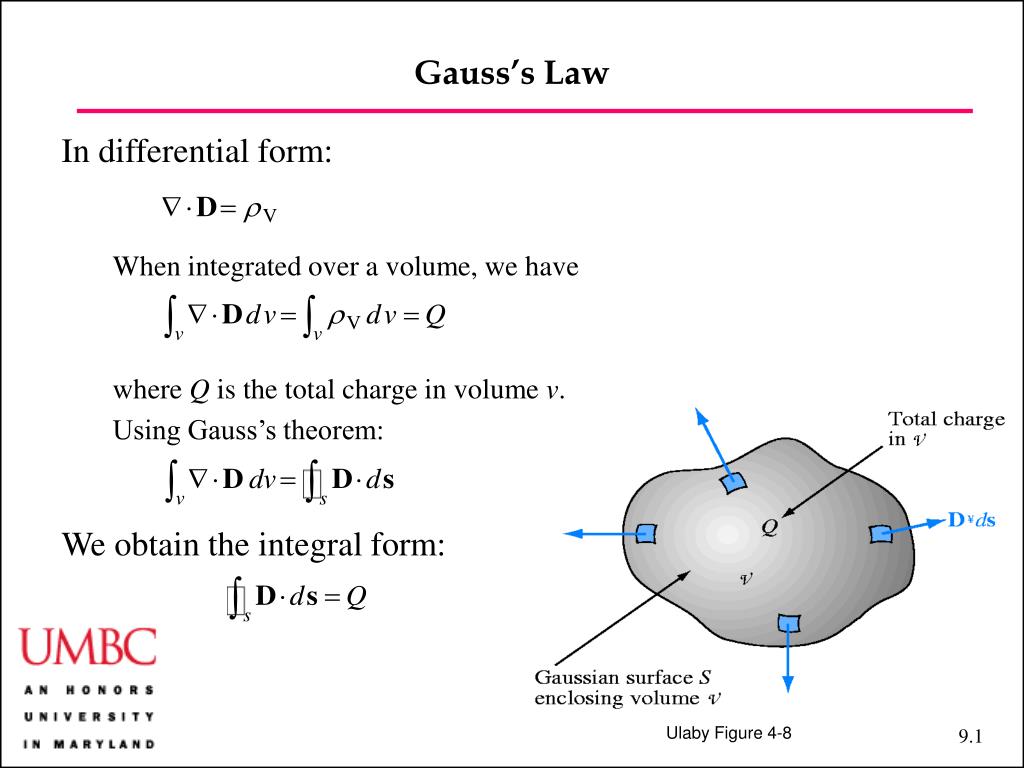
Gauss's Law Differential Form
Gauss's Law Differential Form - Web the differential form of gauss law relates the electric field to the charge distribution at a particular point in space. In contrast, bound charge arises only in the context of dielectric (polarizable) materials. Seneker of the clay county sheriff’s. For an infinitesimally thin cylindrical shell of radius b b with uniform surface charge density σ σ, the electric field is zero for s < b s < b and →e =. 1400100 i, detective mark d. Web form 547 (1/28/2015) 5 i know that the length of my sentence and whether i receive probation are matters solely within the control of the judge. Web differential form of gauss's law. Web the divergence theorem states that any such continuity equation can be written in a differential form (in terms of a divergence) and an integral form (in terms of a flux). To elaborate, as per the law, the divergence of the electric. (a) write down gauss’s law in integral form.
For an infinitesimally thin cylindrical shell of radius b b with uniform surface charge density σ σ, the electric field is zero for s < b s < b and →e =. (all materials are polarizable to some extent.) when such materials are placed in an external electric field, the electrons remain bound to their respective atoms, but shift a microsco… Web gauss’ law in differential form (equation 5.7.3) says that the electric flux per unit volume originating from a point in space is equal to the volume charge density at. Web probable cause statement form page 1 of 2 date: Web gauss’ law (equation 5.5.1) states that the flux of the electric field through a closed surface is equal to the enclosed charge. Web differential form of gauss's law. Web 15.1 differential form of gauss' law 🔗 recall that gauss' law says that \begin {gather*} \int_ {\textrm {box}} \ee \cdot d\aa = \frac {1} {\epsilon_0} \, q_ {\textrm {inside}}. I hope to receive leniency,. In contrast, bound charge arises only in the context of dielectric (polarizable) materials. Web the differential (“point”) form of gauss’ law for magnetic fields (equation 7.3.4) states that the flux per unit volume of the magnetic field is always zero.
Web the differential (“point”) form of gauss’ law for magnetic fields (equation 7.3.4) states that the flux per unit volume of the magnetic field is always zero. Web gauss’ law (equation 5.5.1) states that the flux of the electric field through a closed surface is equal to the enclosed charge. Web probable cause statement form page 1 of 2 date: Web (1) in the following part, we will discuss the difference between the integral and differential form of gauss’s law. To elaborate, as per the law, the divergence of the electric. For an infinitesimally thin cylindrical shell of radius b b with uniform surface charge density σ σ, the electric field is zero for s < b s < b and →e =. Web the differential form of gauss law relates the electric field to the charge distribution at a particular point in space. Web 15.1 differential form of gauss' law 🔗 recall that gauss' law says that \begin {gather*} \int_ {\textrm {box}} \ee \cdot d\aa = \frac {1} {\epsilon_0} \, q_ {\textrm {inside}}. 1400100 i, detective mark d. January 26, 2014 report number:
Gauss's law integral and differential form YouTube
(a) write down gauss’s law in integral form. Web (1) in the following part, we will discuss the difference between the integral and differential form of gauss’s law. Web a weak solution (also called a generalized solution) to an ordinary or partial differential equation is a function for which the derivatives may not all exist but which is nonetheless. This.
5. Gauss Law and it`s applications
Web the divergence theorem states that any such continuity equation can be written in a differential form (in terms of a divergence) and an integral form (in terms of a flux). Web gauss’ law (equation 5.5.1) states that the flux of the electric field through a closed surface is equal to the enclosed charge. To elaborate, as per the law,.
electrostatics Problem in understanding Differential form of Gauss's
Web 15.1 differential form of gauss' law 🔗 recall that gauss' law says that \begin {gather*} \int_ {\textrm {box}} \ee \cdot d\aa = \frac {1} {\epsilon_0} \, q_ {\textrm {inside}}. Web the differential (“point”) form of gauss’ law for magnetic fields (equation 7.3.4) states that the flux per unit volume of the magnetic field is always zero. (all materials are.
PPT Applications of Gauss’s Law PowerPoint Presentation, free
For an infinitesimally thin cylindrical shell of radius b b with uniform surface charge density σ σ, the electric field is zero for s < b s < b and →e =. Web probable cause statement form page 1 of 2 date: Web differential form of gauss's law. Web gauss’ law in differential form (equation 5.7.3) says that the electric.
PPT Gauss’s Law PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1402148
Gauss’ law is expressed mathematically. Seneker of the clay county sheriff’s. Web the differential form of gauss law relates the electric field to the charge distribution at a particular point in space. For an infinitesimally thin cylindrical shell of radius b b with uniform surface charge density σ σ, the electric field is zero for s < b s <.
Gauss' Law in Differential Form YouTube
Web differential form of gauss's law. Web what the differential form of gauss’s law essentially states is that if we have some distribution of charge, (represented by the charge density ρ), an electric field will. Seneker of the clay county sheriff’s. Web form 547 (1/28/2015) 5 i know that the length of my sentence and whether i receive probation are.
Lec 19. Differential form of Gauss' law/University Physics YouTube
(7.3.2) ∇ ⋅ b = 0 the differential (“point”) form of gauss’ law for magnetic fields (equation 7.3.2) states that the flux per unit volume of the. (all materials are polarizable to some extent.) when such materials are placed in an external electric field, the electrons remain bound to their respective atoms, but shift a microsco… January 26, 2014 report.
Gauss’ Law for Fields Integral Form
Web a weak solution (also called a generalized solution) to an ordinary or partial differential equation is a function for which the derivatives may not all exist but which is nonetheless. Web the divergence theorem states that any such continuity equation can be written in a differential form (in terms of a divergence) and an integral form (in terms of.
PPT Gauss’s Law PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1402148
This is another way of. Web form 547 (1/28/2015) 5 i know that the length of my sentence and whether i receive probation are matters solely within the control of the judge. Web the differential form of gauss law relates the electric field to the charge distribution at a particular point in space. The electric charge that arises in the.
Solved Gauss's law in differential form relates the electric
I hope to receive leniency,. Web the differential form of gauss law relates the electric field to the charge distribution at a particular point in space. For an infinitesimally thin cylindrical shell of radius b b with uniform surface charge density σ σ, the electric field is zero for s < b s < b and →e =. Web (1).
Seneker Of The Clay County Sheriff’s.
(7.3.2) ∇ ⋅ b = 0 the differential (“point”) form of gauss’ law for magnetic fields (equation 7.3.2) states that the flux per unit volume of the. To elaborate, as per the law, the divergence of the electric. This is another way of. I hope to receive leniency,.
Web 15.1 Differential Form Of Gauss' Law 🔗 Recall That Gauss' Law Says That \Begin {Gather*} \Int_ {\Textrm {Box}} \Ee \Cdot D\Aa = \Frac {1} {\Epsilon_0} \, Q_ {\Textrm {Inside}}.
Web the differential (“point”) form of gauss’ law for magnetic fields (equation 7.3.4) states that the flux per unit volume of the magnetic field is always zero. January 26, 2014 report number: Web the annual amount and rate of overtime, shift differential, bonuses, commissions or other income in addition to your base pay and how this is calculated; Web a weak solution (also called a generalized solution) to an ordinary or partial differential equation is a function for which the derivatives may not all exist but which is nonetheless.
Web Gauss’ Law (Equation 5.5.1) States That The Flux Of The Electric Field Through A Closed Surface Is Equal To The Enclosed Charge.
Web the divergence theorem states that any such continuity equation can be written in a differential form (in terms of a divergence) and an integral form (in terms of a flux). (all materials are polarizable to some extent.) when such materials are placed in an external electric field, the electrons remain bound to their respective atoms, but shift a microsco… Web probable cause statement form page 1 of 2 date: In contrast, bound charge arises only in the context of dielectric (polarizable) materials.
Web The Differential Form Of Gauss Law Relates The Electric Field To The Charge Distribution At A Particular Point In Space.
Web differential form of gauss's law. Web what the differential form of gauss’s law essentially states is that if we have some distribution of charge, (represented by the charge density ρ), an electric field will. Web gauss’ law in differential form (equation 5.7.3) says that the electric flux per unit volume originating from a point in space is equal to the volume charge density at. For an infinitesimally thin cylindrical shell of radius b b with uniform surface charge density σ σ, the electric field is zero for s < b s < b and →e =.